Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
Healthy Türkiye helps you find the best peritoneal dialysis in Turkey at affordable prices and adopts a 360-degree service approach in all areas of health through affiliated hospitals.
- Homepage
- Medical Treatment
- Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey

About Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
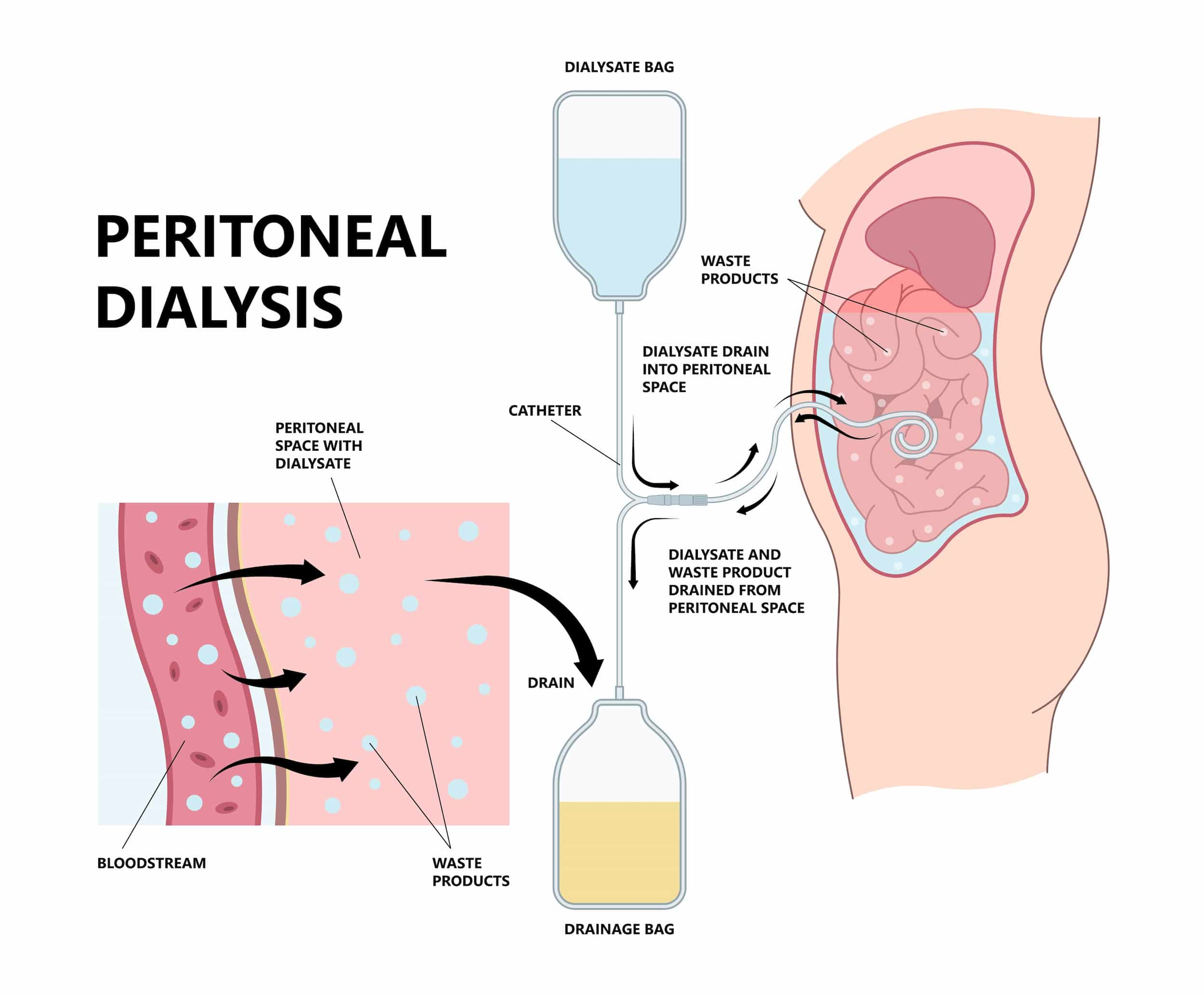
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) in Turkey is a way to remove waste products from your blood when your kidneys can’t adequately do the job any longer. This procedure filters the blood in a different way than the more common blood-filtering procedure called hemodialysis. During peritoneal dialysis, a cleansing fluid flows through a tube, which is called a catheter, into part of your abdomen. The lining of your abdomen (peritoneum) acts as a filter and removes wastes from your blood. After a set period of time, the fluid with the filtered wastes flows out of your abdomen and is discarded.
Peritoneal dialysis can be used at home, at work, or while traveling. But in Turkey, peritoneal dialysis isn’t an option for everyone with kidney disease. You should manual dexterity and the ability to care for yourself at home or you may need a reliable caregiver.
The process of first draining the used dialysis solution and then replacing it with the fresh solution is called an exchange. Mostly, people do four to six exchanges every day, or during the night using a machine that moves the fluid in and out. The process goes on continuously, so you always have dialysis solution in your belly soaking up wastes and extra fluid from the body. For the best results from peritoneal dialysis, it is important that you perform all of your exchange procedures as your doctor instructs.
Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure in Turkey
In this form of treatment, the cleaning function of the kidneys is supported or carried out by the peritoneum of the abdominal cavity. A minor surgical procedure is used to permanently insert a catheter into the abdominal cavity. Through this catheter, a special watery solution is introduced into the abdominal cavity that binds wastes, which are filtered through the peritoneum. The solution for peritoneal dialysis is a sterile fluid mainly consisting of glucose or amino acids which help with waste removal by the peritoneum.
After several hours, the dialysis solution is saturated with wastes from the blood and is drained from the abdomen, then replaced by a fresh solution in order to continue the cleaning. This cycle is generally repeated about four times a day but can also be performed once per day under special circumstances. This procedure must be performed carefully to avoid risks like peritonitis which is an infection of the peritoneum, however, it is easy to learn. That is why patients can carry out this form of dialysis unassisted and in the comfort of their own homes.
Peritoneal dialysis works by using the lining of the abdomen as a filter. There are three stages to a dialysis exchange:
Fill: The abdomen is filled with dialysate. The amount of fluid varies but is generally worked out according to your weight.
Dwell: The dialysis fluid stays in the abdomen for a period of time, which varies from patient to patient and depends on the type of peritoneal dialysis used. During this time, wastes and chemicals pass from the tiny blood vessels next to the lining of the abdomen into the fluid.
Drain: The used dialysis fluid is drained from your body and discarded.

We Care About Your Health
Healthy Türkiye provides the best for your health and comfort. You will feel privileged with us.
7/24 Quality Personal Assistance Throughout Your Journey
Customizable for You All-Inclusive Packages
Get the Right Advice for your Health
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
There are 2 types of peritoneal dialysis (PD) in Turkey: continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD). Both types of peritoneal dialysis have slightly different advantages, so it really comes down to your personal preference and schedule along with your specialist’s recommendation. The form of peritoneal dialysis that is best for each patient depends on their lifestyle, personal preferences, and medical condition. Some patients can use a customized program that combines the two forms.
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
CAPD is peritoneal dialysis turkey that can be done manually, without a machine, throughout the day. The patient fills the abdomen with a dialysis solution and later drains the fluid. In this procedure, gravity moves the fluid through the tube and into and out of the belly.
Each exchange cycle includes filling the abdomen with dialysate fluid, letting the fluid dwell in the abdomen, and then draining the fluid. Patients usually need three to four exchanges during the day and one with a longer dwell time while sleeping. Exchanges can be done at home, on holiday, or in any clean place. During CAPD, patients are able to go about their normal activities while the dialysis solution dwells in their abdomen between exchanges.
Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD)
With CCPD, which can also be called automated peritoneal dialysis (APD), a machine called an automated cycler performs three to five exchanges at night while the patient sleeps. The cycler automatically fills the abdomen with dialysis solution, allows it to dwell there, and then drains it into a sterile drainage bag that is then discarded in the morning. This gives patients more flexibility during the day, but they must remain attached to the machine for 10 to 12 hours at night. In the morning patients begin one exchange with a dwell time that lasts the entire day.
You can get information about the whole peritoneal dialysis procedure by contacting Healthy Türkiye. With our expert team, you can discuss which option is most suitable for your needs.
Prepare for Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
Surgery to put in your catheter: Before your peritoneal dialysis treatment, you will have surgery to place a catheter into your belly. You should be planning your catheter placement at least 3 weeks before your first exchange can improve treatment success. Even if you can use the catheter as soon as it’s in place, the catheter tends to work better when you have 10 to 20 days to heal before starting a full schedule of exchanges.
The surgeon will make a small cut, often below and a little to the side of your belly button, and then guide the catheter through the slit into your peritoneal cavity. You’ll receive general or local anesthesia, and you might need to stay overnight in the hospital. However, most patients can go home after the procedure. Also, you should learn to care very well for the skin around the catheter, called the exit site, as part of your dialysis training.
Dialysis training: After the training procedure, most people can perform both types of peritoneal dialysis on their own. You should work with a dialysis nurse for 1 to 2 weeks to learn how to do exchanges and avoid infections. Mostly, people bring a family member or friend to training. With a trained friend or family member, you should be prepared in case you have a sick day and need help with exchanges.
If you choose automated peritoneal dialysis, you’ll learn step-to-step how to:
Prepare the cycler
Connect the bags of dialysis solution
Place the drain tube
If you choose automated peritoneal dialysis, you must learn how to do exchanges by hand in case of a power failure or if you need an exchange during the day in addition to nighttime automated peritoneal dialysis.
How to Perform an Exchange?
During the exchange process you’ll need the following supplies:
Transfer set
Dialysis solution
Supplies to keep your exit area clean
Also if you choose automated peritoneal dialysis you’ll need a cycler.
Your healthcare team will provide everything you need to begin peritoneal dialysis. Firstly, careful hand washing and wearing a surgical mask over your nose and mouth while you connect your catheter to the transfer set can help prevent infection.
Transfer Set: The transfer set is tubing that you use to connect your catheter to the bag of dialysis solution. When you first get your catheter, the section of tube that sticks out from your skin should have a secure cap on the end to prevent infection. The connector under the cap will attach to any type of transfer set. The permanent catheter connects to the transfer set, which has a disposable cap. Y-shaped disposable tubing has one branch coming from a hanging bag of fresh solution and one branch going to a drain bag, both branches have clamps.
You should connect the catheter to the transfer set for your exchange. Between exchanges, you can keep your catheter and transfer set hidden inside the clothing. At the beginning of an exchange, you should remove the disposable cap from the transfer set and connect the set to a tube that branches like the letter Y. So, one branch of the Y-tube connects to the drain bag, while the other connects to the bag of fresh dialysis solution.
Dialysis Solution: Dialysis solution is 1.5-, 2-, 2.5-, or 3-liter bags. Solutions contain a sugar called dextrose or a compound called icodextrin and minerals to pull the wastes and extra fluid from your blood into the belly. Different solutions have different strengths of dextrose or icodextrin, your doctor will prescribe a formula that fits your needs.
Clean Area: You should store your solution bags and other supplies in a clean area. Thus, you will minimize side effects such as infection.
Cycler for Automated Peritoneal Dialysis Exchanges: In the automated peritoneal dialysis method, you use a machine called a cycler to fill and drain your belly. You can program the cycler to give you different amounts of dialysis solution at different times.
Each evening, you can set up the machine to do three to five exchanges for you. You should connect three to five bags of dialysis solution to tubing that goes into the cycler, one bag of solution for each exchange. The machine might have a special tube to connect the bag for the last exchange of the night. Lines connect the dialysis solution to the person, the drain line connects from the person and out of the frame of the drawing.
The automated peritoneal dialysis machine fills and empties your belly three to five times during the night while you sleep. At the times you set, the cycler releases a clamp and allows the used solution to drain out of your belly into the drain line warms the fresh dialysis solution before it enters your body and releases a clamp to allow the body-temperature solution to flow into your belly. The fluid meter in the cycler measures and records how much solution the cycler removes, also, some cyclers compare the amount that was put in with the amount that drains out. This way lets you and your doctor know if the treatment is removing enough fluid from your body.
Besides, some cyclers allow you to use a long drain line that drains directly into your toilet or bathtub and others have a disposal container.
Doing an Exchange By Hand
Firstly, you should wash your hands and put on your surgical mask, then drain the used dialysis solution from your belly into the drain bag. Near the end of the drain, you can feel a mild tugging sensation that tells you most of the fluid is gone. At this point, you should close the transfer set.
You should warm each bag of solution to body temperature before use. For this, you can use an electric blanket, or let the bag sit in a tub of warm water. Solution bags often come in a protective outer wrapper, and you can warm them in a microwave. But you shouldn’t microwave a bag of solution after you have removed it from its wrapper.
Then, you should hang the new bag of solution on a pole and connect it to the tubing. Remove air from the tubes, and allow a small amount of fresh, warm solution to flow directly from the new bag of solution into the drain bag. Next, clamp the tube that goes to the drain bag. Open the transfer set, and refill your belly with fresh dialysis solution from the hanging bag.
Living with Peritoneal Dialysis
Chronic kidney disease is a condition that requires lifelong treatment. Peritoneal dialysis is one option for lifelong treatment, with other options such as hemodialysis and kidney transplantation. It is sometimes necessary to switch type one type of treatment to another as circumstances change.
Diet: People who undergo peritoneal dialysis are often required to make changes to their diet. In general, patients who use peritoneal dialysis have a less restricted diet compared with those who use standard in-center hemodialysis. Dietary changes help to ensure that the body has an adequate, but not excessive, amount of protein and minerals.
People who use peritoneal dialysis lose protein with every exchange, which usually means that they must eat an increased amount of protein in their diet. Proteins are found in meat, milk, chicken, fish, and eggs; lower-quality proteins are found in some vegetables and grains. A dietitian can provide specific recommendations about how much and what kind of protein is needed.
Other changes in diet may include reducing the number of foods eaten that contain phosphorus (found in dairy products, cheese, dried beans, liver, nuts, and chocolate) and sodium and monitoring the number of fluids consumed.
Weight gain: Weight gain can be a problem for people undergoing peritoneal dialysis because the dialysate contains a high concentration of dextrose, a kind of sugar. The body absorbs some of this dextrose during the dwelling, which can lead to weight gain. The dietitian can provide guidance on how to minimize weight gain by monitoring the number of calories eaten.
Body image: The abdomen may enlarge slightly and may cause you to feel bloated when it is filled with fluid, although most people do not look physically different from others. You may need a larger size of clothing and see a physical difference when dressed, some people have a hard time accepting the change in their appearance. Patient support groups and websites can provide tips for dressing.
Activities and peritoneal dialysis: People generally using peritoneal dialysis should limit physical activities when their peritoneal cavity is full (has a large-volume dwell). It is still possible to exercise and participate in sports, although you should discuss your activities with your doctors.
Time requirements: Peritoneal dialysis requires time and dedication, interfering with other activities. This is true with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD), which requires the person to perform several exchanges during the daytime. Although it is possible to work and be active while using peritoneal dialysis, it might be necessary to cut back on responsibilities.
It is important to perform every exchange and dwell exactly as recommended. Skipping a treatment or performing a dwell for shorter or longer than recommended may increase the risk of illness and the chances of being hospitalized and can even shorten the patient’s life.
What is Peritonitis?
Peritonitis is an infection inside the abdominal space. It is often caused by common bacteria that live on the skin or in the intestines. Most episodes of peritonitis occur because of accidental contamination of the peritoneal fluid, and can generally be avoided by strictly following the proper techniques taught during the initial peritoneal dialysis training. Peritonitis was once a common and dreaded complication of PD, however, technology and techniques have improved so peritonitis is now much less common. In Turkey, many patients on peritoneal dialysis go for years without ever getting peritonitis. In most PD programs, the average patient will have less than one episode of peritonitis every two years on therapy.
Peritonitis can be painful, so, prevention is very important. For this, strict hand washing, the use of a mouth/nose mask, and proper sterile exchange technique are critical. Daily application of antibiotic cream to the catheter exit area should be performed since it has been shown to reduce the frequency of infections. Besides, any possible contamination of your dialysis fluid or catheter should be reported immediately to your peritoneal dialysis healthcare team.
If your fluid becomes cloudy, especially if accompanied by fever, nausea, or abdominal pain, you should call the peritoneal dialysis healthcare team right away. These might be signs of peritonitis, and starting treatment quickly can often prevent the problem from getting worse. Peritonitis problems can be painful, although most cases can be managed with oral medications and without the need for hospitalization. Peritonitis requires 2-3 weeks of therapy and usually involves the use of antibiotics that are added to one of your daily dialysis fluid exchanges.
2026 Cost of Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
All types of medical attention like peritoneal dialysis are very affordable in Turkey. Many factors are also included in determining the cost of dialysis in Turkey. Your process with Healthy Türkiye will last from the time you decide to have kidney disease in Turkey until the time you are fully recovered even if you are back home. The exact peritoneal dialysis procedure cost in Turkey depends on the type of operation involved.
The cost of peritoneal dialysis in Turkey does not demonstrate many variations in 2022. Compared to costs in developed countries like the United States or the UK, dialysis costs in Turkey are relatively low. So, it’s no wonder patients from across the world visit Turkey for peritoneal dialysis procedures. However, the cost is not the only factor affecting choices. We suggest looking for hospitals that are safe and have peritoneal dialysis reviews on Google. When people decide to seek medical help for kidney disease, they will not only have low-cost procedures in Turkey, but also the safest and best treatment.
At clinics or hospitals contracted with Healthy Türkiye, patients will receive the best peritoneal dialysis from specialist doctors in Turkey at affordable rates. Healthy Türkiye teams to provide medical attention dialysis procedures and high-quality treatment to patients at a minimum cost. When you contact Healthy Türkiye assistants, you can get free information about the cost of peritoneal dialysis in Turkey and what this cost covers.
Why Choose Turkey for Peritoneal Dialysis?
Turkey is a common choice among international patients seeking advanced dialysis procedures. Turkey’s health procedures are safe and effective operations with a high success rate like peritoneal dialysis. The increasing demand for high-quality peritoneal dialysis at affordable prices has made Turkey a popular medical travel destination. In Turkey, peritoneal dialysis is performed by highly experienced and trained doctors with the most advanced technology in the world. Dialysis procedure is done in Istanbul, Ankara, Antalya, and other major cities. The reasons for choosing peritoneal dialysis in Turkey are as follows:
High-quality hospitals: Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited hospitals have dedicated peritoneal dialysis units that are specially designed for patients. International and national strict protocols provide effective and successful peritoneal dialysis for patients in Turkey.
Qualified experts: The expert teams include nurses and specialist doctors, together to carry out peritoneal dialysis according to the patient’s needs. All the included doctors are highly experienced in performing peritoneal dialysis.
Affordable price: The cost of peritoneal dialysis turkey is affordable compared to Europe, the USA, the UK, Singapore, and Australia.
The high success rate: Highly experienced specialists, the best available technology, and stringently followed safety guidelines for post-operative care of the patient, resulting in a high success rate for peritoneal dialysis in Turkey.
All-Inclusive Package for Peritoneal Dialysis in Turkey
Healthy Türkiye offers all-inclusive packages for peritoneal dialysis in Turkey at much lower prices. Extremely professional and experienced doctors and technicians carry out high-quality dialysis. The cost of peritoneal dialysis in European countries can be quite expensive, especially in the UK. Healthy Türkiye provides cheap all-inclusive packages for a long and short stay of dialysis in Turkey. Because of many factors, we can provide you with many opportunities for your kidney disease in Turkey.
The price of peritoneal dialysis differs from other countries due to medical fees, staff labor prices, exchange rates, and market competition. You can save much more in peritoneal dialysis compared to other countries in Turkey. When you purchase peritoneal dialysis all-inclusive package with Healthy Türkiye our healthcare team will present hotels for you to choose from. In dialysis travel, you will have the price of your stay included in the all-inclusive package cost.
In Turkey, when you purchase peritoneal dialysis all-inclusive packages through Healthy Türkiye, you will always receive VIP transfers. These are provided by Healthy Türkiye, which is contracted with highly qualified hospitals for peritoneal dialysis in Turkey. Healthy Türkiye teams will organize everything about peritoneal dialysis for you and have you picked up from the airport and safely brought to your accommodation.
Once settled in the hotel, you will be transferred to and from the clinic or hospital for peritoneal dialysis. After your peritoneal dialysis has been successfully completed, the transfer team will return you to the airport in time for your flight home. All packages of peritoneal dialysis turkey can be arranged upon request, which relaxes the minds of our patients. You can reach out Healthy Türkiye for everything you need to know about peritoneal dialysis in Turkey.
The Best Hospitals in Turkey for Peritoneal Dialysis
The best hospitals in Turkey for peritoneal dialysis are Healthy Türkiye, Memorial Hospital, Acıbadem International Hospital, and Medicalpark Hospital. These hospitals attract patients from all over the world seeking peritoneal dialysis due to their affordable prices and high success rates.
Best Doctors and Surgeons in Turkey for Peritoneal Dialysis
The best doctors and surgeons in Turkey for peritoneal dialysis are highly skilled professionals who offer specialized care and advanced procedures. With their expertise and state-of-the-art techniques, these specialists ensure that patients receive high-quality peritoneal dialysis and achieve optimal health results.

Frequently Asked Questions
The average life expectancy on peritoneal dialysis is 5-10 years, however, many patients have lived well on dialysis for 20 or even 30 years.
There are 2 types of peritoneal dialysis (PD): continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD). Both types of peritoneal dialysis have slightly different advantages, so it really comes down to your personal preference and schedule along with your specialist’s recommendation.
The Dietitians encourage most people on peritoneal dialysis to eat high-quality protein because it produces less waste, which has to be removed during dialysis, high-quality protein comes from meat, poultry, fish, and eggs.
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis is the most common type of PD, it can be done in any place that’s clean and well-lit. This kind of self-dialysis is done 7 days a week. Four to five exchanges of the new solutions are done each day.
There are multiple at-home dialysis treatment options, many patients perform peritoneal dialysis at home with no assistance.
Dialysate flows into your abdomen and stays there for a prescribed period of time (dwell time), usually four to six hours.
There are two forms of dialysis: peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD), both of which can be done at night while you sleep.
The most frequent and important complication of peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheters is an infection, which may result in catheter loss and discontinuation of PD.
