Mammogram Techniques
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), breast cancer is the second most common cancer among women worldwide, and the most common cancer among women in many countries. However, early detection of breast cancer can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery. Mammography is a screening test that is commonly used to detect breast cancer. In this article, we will provide an overview of the best mammogram techniques, particularly the shift from 2D to 3D mammography.
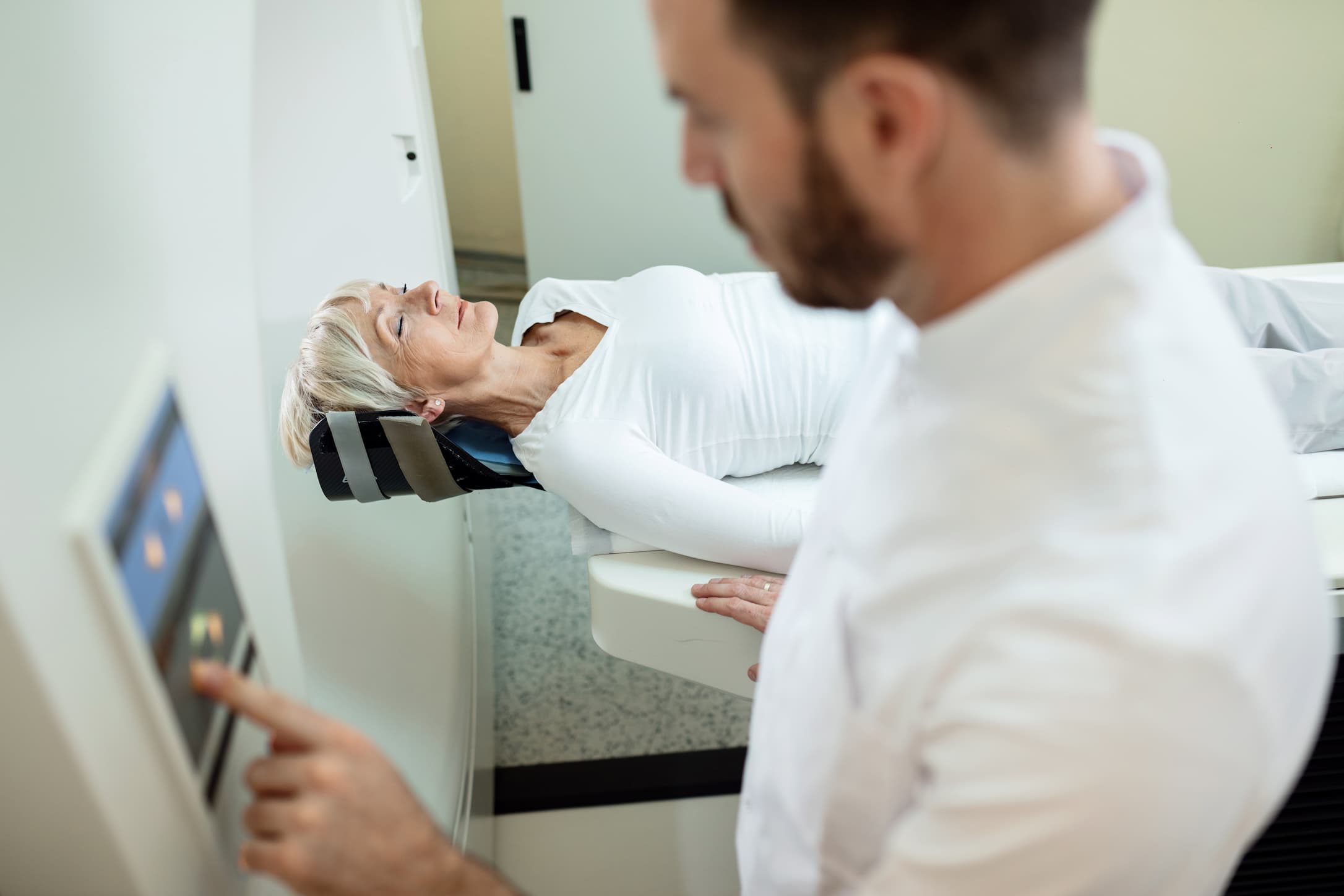
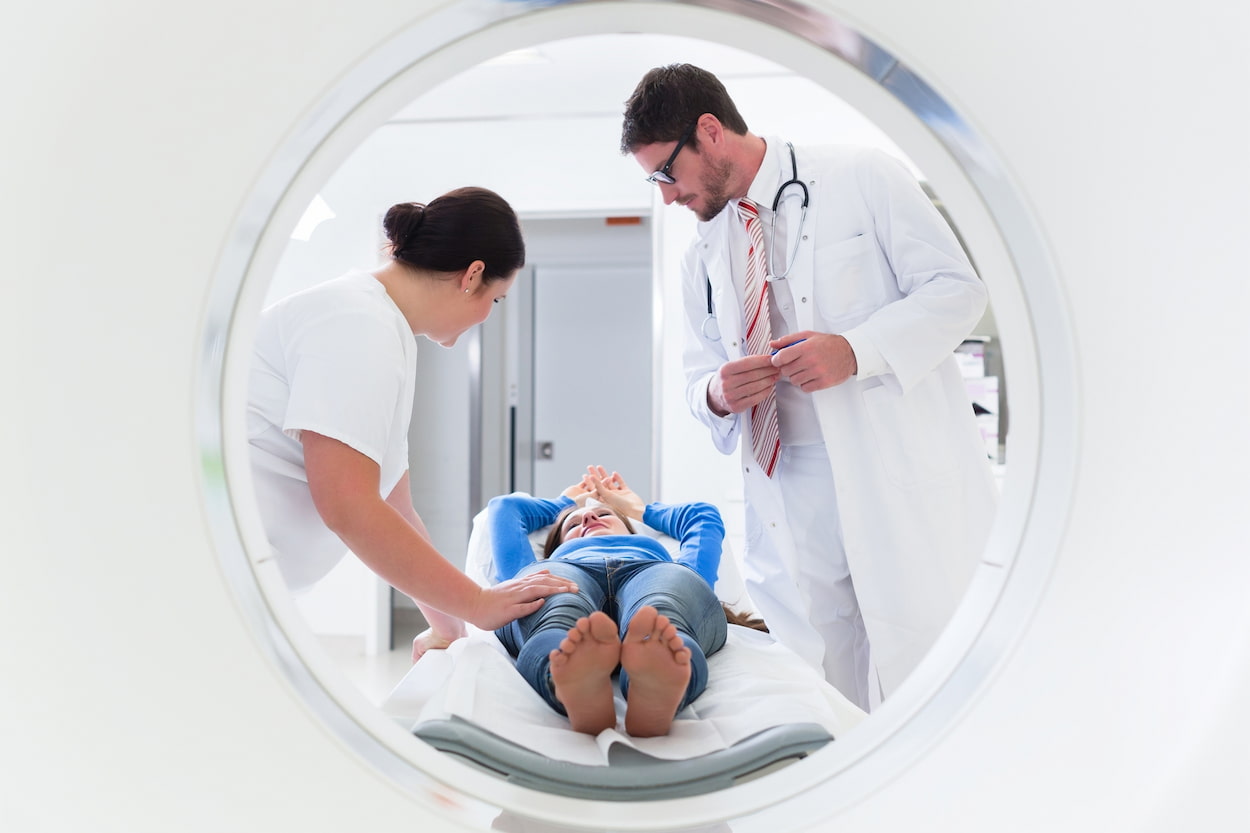
Mammography is a type of X-ray imaging that is used to examine the breast for any signs of abnormality, including lumps or masses. Mammograms can detect breast cancer at an early stage, even before a lump can be felt. Mammography is recommended for women who are at average risk of breast cancer between the ages of 50 and 74, and for women who are at high risk of breast cancer, including those with a family history of breast cancer or certain genetic mutations.
Traditionally, mammography has been done using 2D imaging, which produces a flat image of the breast tissue. However, 2D mammography has some limitations, including the possibility of overlapping tissue, which can make it difficult to see small abnormalities. This can lead to false positives, which require additional imaging tests and can cause anxiety and stress for the patient.
3D mammography, also known as tomosynthesis, is a newer technology that provides a more detailed and accurate view of the breast tissue. In 3D mammography, the breast is imaged in multiple thin slices, which are then reconstructed into a 3D image. This allows for a clearer view of the breast tissue and can help to detect small abnormalities that might not be visible on 2D mammography.
One of the main advantages of 3D mammography is that it reduces the need for additional imaging tests. Studies have shown that 3D mammography can reduce the number of false positives by up to 40%, which means that fewer women need to undergo additional imaging tests or biopsies.
Another advantage of 3D mammography is that it can detect breast cancer at an earlier stage than 2D mammography. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2014 found that 3D mammography detected 41% more invasive breast cancers than 2D mammography. This is because 3D mammography provides a more detailed view of the breast tissue, which can help to identify small cancers that might be missed on 2D mammography.
In addition, 3D mammography is particularly beneficial for women with dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue is a common risk factor for breast cancer and can also make it more difficult to detect small abnormalities on 2D mammography. 3D mammography can provide a clearer view of the breast tissue in women with dense breasts, which can improve the accuracy of the screening test.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to 3D mammography. One of the main concerns is that it exposes women to more radiation than 2D mammography. Although the radiation dose from 3D mammography is still within safe limits, some women may be hesitant to undergo additional radiation exposure.
Another concern is the cost of 3D mammography. 3D mammography machines are more expensive than 2D mammography machines, and the cost of the test may be higher as a result. However, many insurance plans now cover the cost of 3D mammography, and the benefits of the test may outweigh the additional cost.
In summary, mammography is an important screening test for breast cancer, and early detection is key to successful treatment and recovery. 3D mammography is a newer technology that provides a more detailed and accurate view of the breast tissue, which can improve the accuracy of the screening test and reduce the need for additional imaging tests. While there are some potential drawbacks to 3D mammography, the benefits of the test may outweigh the risks for many women. Women should discuss the pros and cons of 3D mammography with their healthcare provider to determine the best screening option for their individual needs.
Differences Between 2d To 3d In Mammography
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women globally, and mammography is a screening test that is commonly used to detect breast cancer. Mammography is an X-ray imaging technique that produces images of breast tissue, allowing doctors to detect any abnormalities, including lumps or masses, that may be an indication of breast cancer.
Traditionally, mammography has been done using 2D imaging, which produces a flat image of the breast tissue. However, 2D mammography has some limitations that can lead to false positives or false negatives, which can be concerning for patients and potentially delay the detection of breast cancer.
3D mammography, also known as tomosynthesis, is a newer technology that provides a more detailed and accurate view of the breast tissue. 3D mammography works by taking multiple images of the breast from different angles, which are then reconstructed into a 3D image. This allows for a more comprehensive view of the breast tissue, reducing the likelihood of missed or misinterpreted abnormalities.
One of the main differences between 2D and 3D mammography is the way the images are obtained. 2D mammography produces a flat image of the breast tissue, which can sometimes result in overlapping tissue that can obscure small abnormalities or cause false positives. In contrast, 3D mammography takes multiple images of the breast tissue at different angles, which are then reconstructed into a 3D image. This provides a more detailed and comprehensive view of the breast tissue, which can help to detect small abnormalities that might not be visible on 2D mammography.
Another difference between 2D and 3D mammography is the accuracy of the screening test. Several studies have found that 3D mammography is more accurate than 2D mammography, particularly for women with dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue can make it more difficult to detect small abnormalities on 2D mammography, whereas 3D mammography can provide a clearer view of the breast tissue and improve the accuracy of the screening test.
In addition, 3D mammography can reduce the need for additional imaging tests. False positives, which occur when an abnormality is detected on a mammogram but turns out not to be cancerous, can lead to additional imaging tests or biopsies, which can be stressful and time-consuming for patients. Studies have shown that 3D mammography can reduce the number of false positives by up to 40%, which can reduce the need for additional testing and reduce patient anxiety.
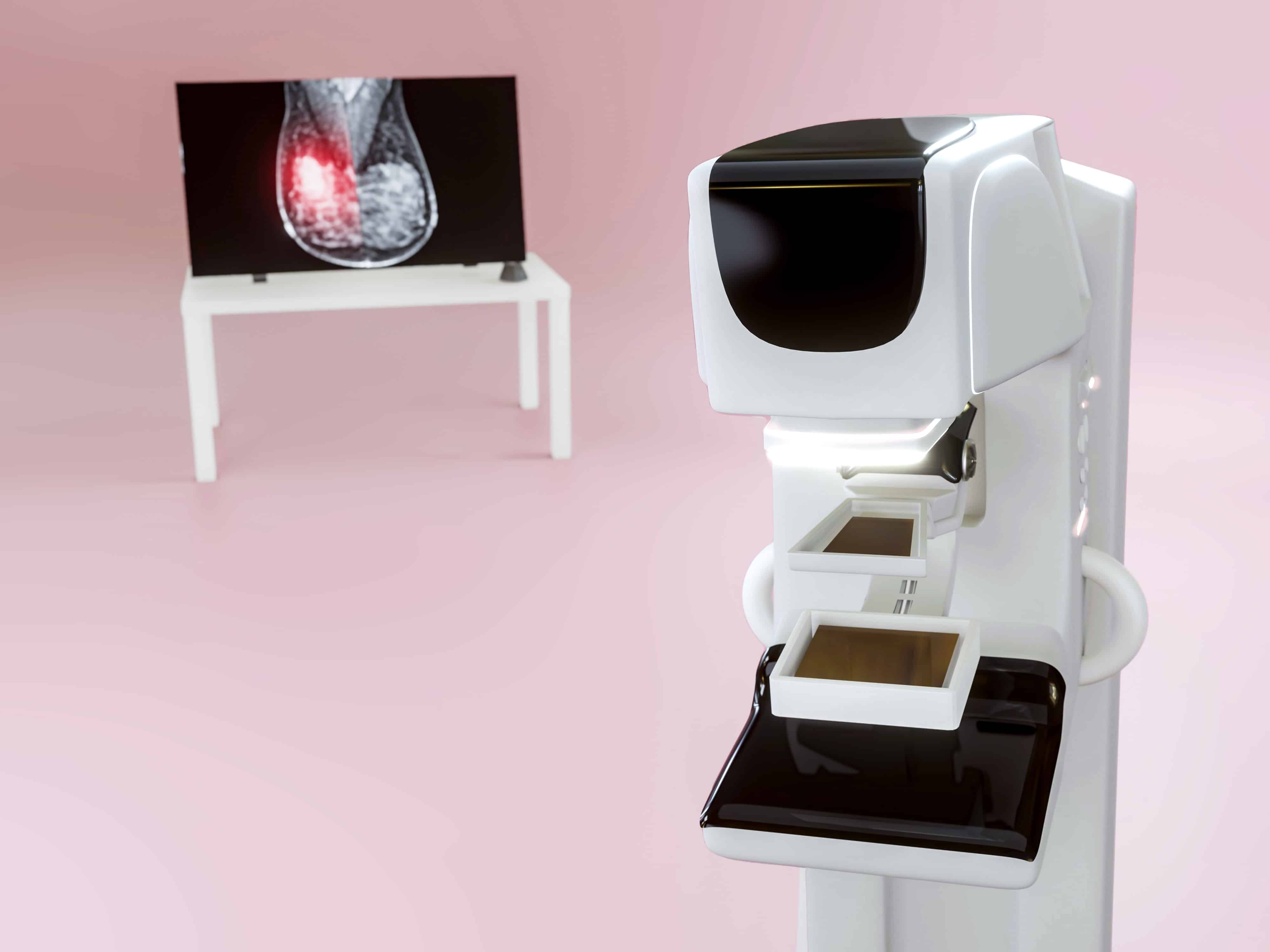
Which Is Better Mammogram or MRI?
When it comes to breast cancer screening, mammograms are considered to be the gold standard test. Mammograms use X-rays to detect any abnormalities or changes in the breast tissue, including small lumps or calcifications that may indicate the presence of cancer. Mammograms are highly effective at detecting breast cancer early, which can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved survival rates. While MRIs can also be used to screen for breast cancer, they are generally reserved for high-risk patients or for follow-up after a mammogram has identified a potential problem. Mammograms are generally more widely available, less expensive, and less time-consuming than MRIs, making them a better option for most women.
The Study of Mammogram Techniques
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2019 compared the performance of 2D and 3D mammography in a large population of women. The study found that 3D mammography detected 27% more breast cancers than 2D mammography, particularly in women with dense breast tissue. This research demonstrates the superior accuracy of 3D mammography in detecting breast cancer, emphasizing its role in early detection and improved patient outcomes.
What Age Is Mammography Recommended?
Mammography is a type of breast cancer screening that uses X-rays to detect any abnormalities or changes in the breast tissue. The age at which mammography is recommended can vary depending on a woman’s risk factors for breast cancer. Generally, women who are at average risk for breast cancer are recommended to begin getting regular mammograms at age 50 and continue to do so every one to two years thereafter. However, women with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors may be advised to begin mammography at an earlier age, usually starting in their 40s. It is important for women to discuss their individual risk factors with their healthcare provider to determine when mammography is appropriate for them.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
In conclusion, mammography is a highly effective screening tool for breast cancer detection. It is generally recommended for women at average risk for breast cancer to begin mammography at age 50 and continue to get regular screenings thereafter. However, for women with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors, earlier and more frequent screenings may be recommended. It is important for women to discuss their individual risk factors with their healthcare provider and follow the recommended screening guidelines to help detect breast cancer early and improve treatment outcomes.
While other screening options such as MRIs may be available, mammography remains the gold standard test for breast cancer detection and is widely available, less expensive, and less time-consuming than other options. Regular mammography screenings can be a lifesaving measure for women, helping to detect breast cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages.