Inside the World of Medical Imaging: The Differences Between MRI and CT Scans
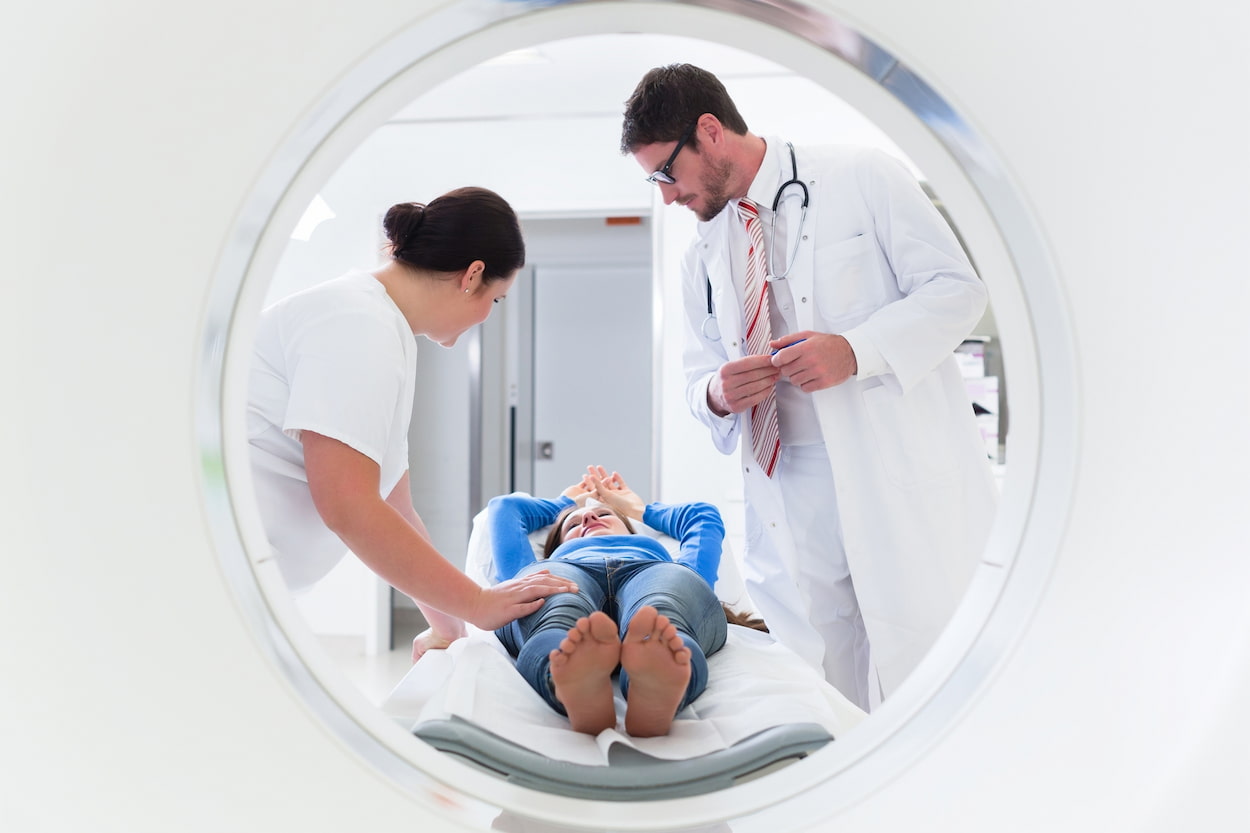
Imaging in medicine is extremely important in both the diagnosis and treatment of a wide variety of medical disorders. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the computed tomography (CT) scan are both examples of common imaging methods that are utilized. Both serve the same goal, but they do so using distinct technologies, have different advantages and disadvantages, and may be better suited to certain circumstances depending on the specifics of those conditions. In this article, we will compare and contrast MRI scans and CT scans, discuss their respective applications, and examine the factors that may lead a physician to choose one over the other.
The Differences Between MRI and CT Scans
Because it enables doctors to see what's happening on the inside of a patient's body, imaging is an essential component of the diagnostic process in the medical field. Imaging treatments such as MRI and CT scans are quite prevalent these days. MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging, and CT stands for computed tomography. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans both perform the same function; however, the former makes use of a different technology, while the latter offers a variety of benefits and drawbacks. In this article, we will examine the similarities and differences between computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, as well as analyze the conditions under which one type of scan would be more appropriate than the other.

CT scan vs. MRI
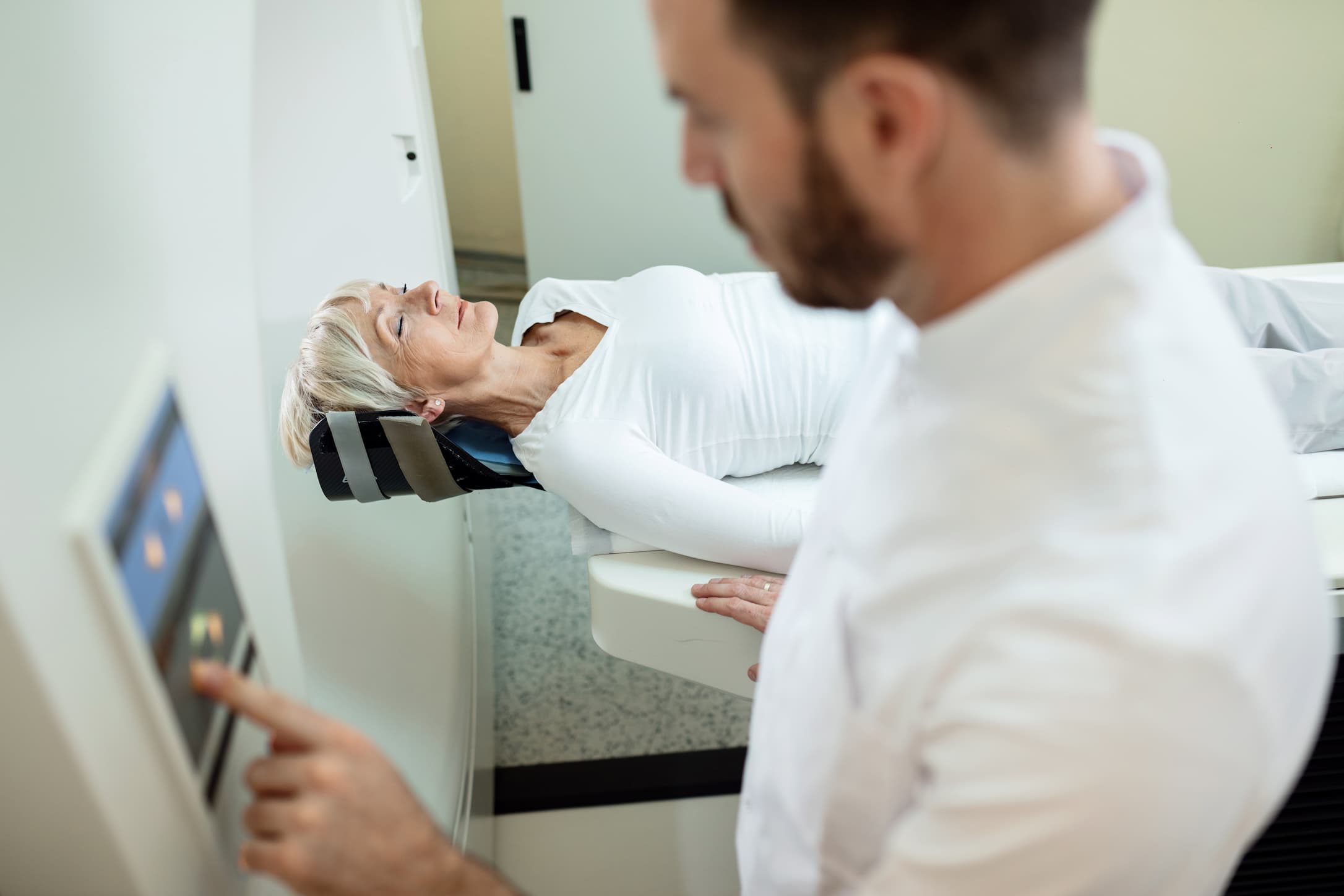
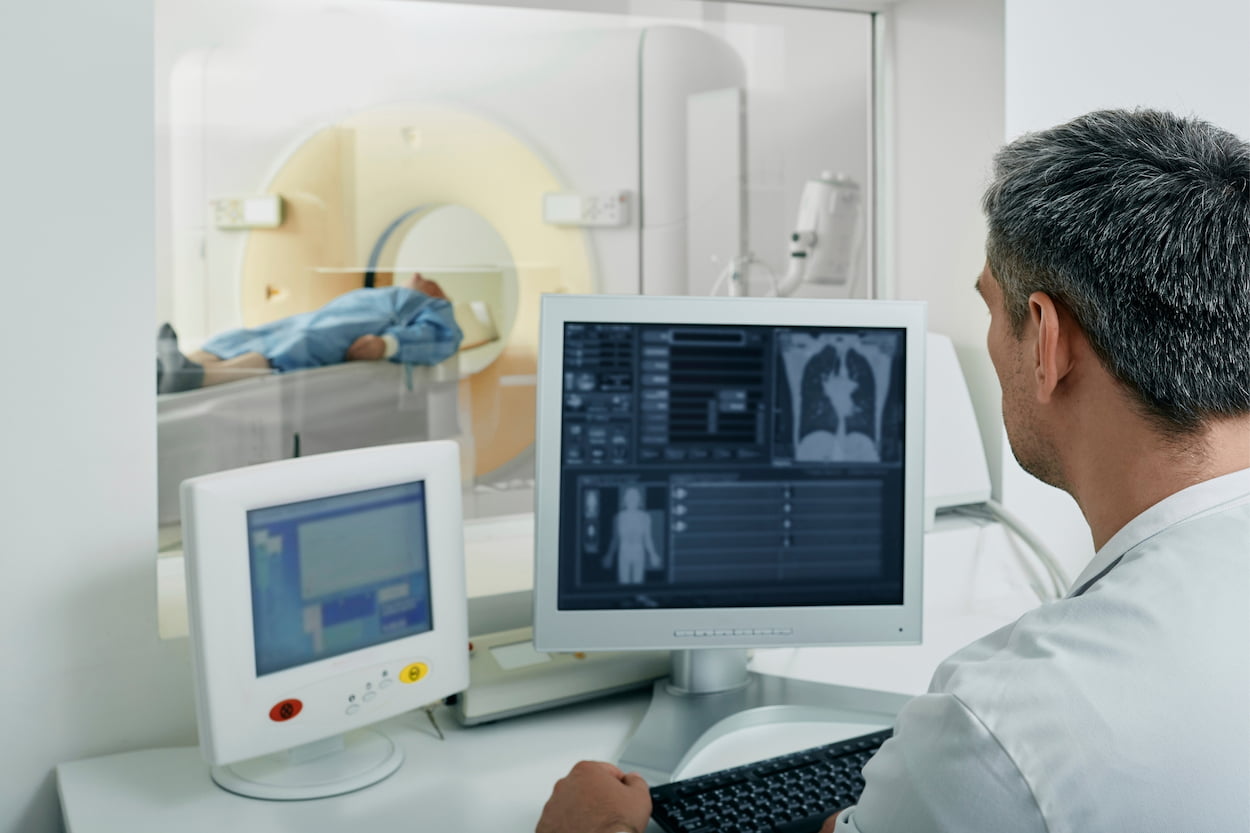
A CT scan (computed tomography) uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of bones, organs, and tissues in the body. The images are created by taking multiple X-ray images from different angles and combining them into a three-dimensional image.
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of internal structures in the body. The technology creates images by detecting the energy released by water molecules in the body.
Difference between MRI and CT scan
One of the main differences between MRI and CT scans is the type of information they provide. CT scans are better at detecting bone damage, tumors, and internal bleeding. They are often used in emergency situations, such as after a car accident, to quickly identify injuries that require immediate treatment.
On the other hand, MRI scans are better at detecting soft tissue injuries, such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and ligament damage. They are also better at imaging organs like the liver, pancreas, and prostate.
MRI vs. CT
Another key difference between MRI and CT scans is the amount of radiation exposure. CT scans expose patients to higher levels of radiation, which can be a concern for frequent scans or for individuals who are particularly sensitive to radiation. MRI scans, on the other hand, do not use ionizing radiation and are generally considered safe for most patients.
Difference between CT and MRI
CT scans are typically completed in less time and can be obtained from a wider variety of locations than MRI scans. They are also less expensive, making them a more cost-effective choice for some scenarios due to the fact that specific circumstances warrant it. MRI scans, on the other hand, might take significantly more time and may not be as easily accessible, especially in more rural and distant places. In most cases, they also come with a higher price tag than CT scans.
What Does a Ct Scan Show that an MRI Does not?
CT scans are particularly good at detecting bone fractures, tumors, and internal bleeding. They are also effective at imaging the lungs and other organs that have high density, such as the liver, pancreas, and spleen. CT scans can often provide more detailed images of these areas than MRI scans.
Why Would a Doctor Order a Ct Scan Instead of An MRI?
A doctor may order a CT scan instead of an MRI if the patient has a suspected bone fracture, internal bleeding, or a tumor. CT scans are faster, more widely available, and less expensive than MRI scans, making them a good option for emergency situations or situations where speed is critical. Additionally, some patients may not be able to undergo an MRI due to metal implants, such as pacemakers or cochlear implants, which can interfere with the MRI's magnetic field.
What Is an MRI Scan Used to Diagnose?
MRI scans are commonly used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including:
Brain and spinal cord injuries or disorders
Soft tissue injuries, such as ligament damage
Tumors
Multiple sclerosis
Stroke
Arthritis
Heart and vascular conditions
Breast cancer
In many cases, an MRI scan can provide more detailed and accurate information than other imaging techniques, making it a valuable tool in diagnosing and treating a wide range of medical conditions.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
Both MRI and CT scans are important imaging techniques that have their own strengths and limitations. While CT scans are better at detecting bone fractures, internal bleeding, and tumors, MRI scans are better at detecting soft tissue injuries and imaging organs. CT scans are faster, more widely available, and less expensive than MRI scans, making them a good option for emergency situations or situations where speed is critical. On the other hand, MRI scans are generally safer and more accurate in providing detailed images, making them a preferred option in many cases.
When it comes to deciding which imaging technique is best for a patient, doctors will take into account several factors, such as the patient's medical history, symptoms, and the suspected condition. They may also consider the patient's preferences and any potential risks associated with each technique. Ultimately, the decision will be based on what will provide the most accurate and useful information for the patient's diagnosis and treatment plan.
In summary, the differences between MRI and CT scans are significant, and both techniques have their own unique strengths and limitations. By understanding these differences, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare and work with their doctors to develop the best treatment plan possible.