The Various Types of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition that affects the spine, causing it to curve sideways instead of remaining straight. This curvature can lead to discomfort and pain, especially if it becomes severe. There are different types of scoliosis, and each one has its unique characteristics and causes.
What Is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. In people with scoliosis, the spine curves to the side, creating a C or S shape, which can cause pain and discomfort, especially if the curvature becomes severe. Scoliosis can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in children and adolescents during their growth spurt.
There are different types of scoliosis, including idiopathic scoliosis, which is the most common type and has no known cause, congenital scoliosis, which is present at birth and is caused by abnormalities in the spine’s development, neuromuscular scoliosis, which is caused by medical conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, and degenerative scoliosis, which is caused by wear and tear on the spine due to aging.
What Causes Scoliosis?
The exact cause of most types of scoliosis is unknown. However, certain factors can increase the risk of developing scoliosis, including:
Family history: scoliosis tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
Age: most cases of scoliosis develop during childhood or adolescence, during the growth spurt.
Gender: girls are more likely to develop scoliosis than boys.
Medical conditions: certain medical conditions, such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, can increase the risk of developing scoliosis.
Different Types of Scoliosis
There are different types of scoliosis, and each one has its unique characteristics and causes. The four main types of scoliosis are:
Idiopathic Scoliosis
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type of scoliosis, accounting for about 80% of all cases. Idiopathic means that the cause of the condition is unknown. This type of scoliosis usually develops in children and adolescents, and it is more common in girls than boys. Idiopathic scoliosis can be further categorized based on the age of onset:
Infantile idiopathic scoliosis: develops in children under three years old.
Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis: develops in children between four and ten years old.
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: develops in children between eleven and eighteen years old.
Congenital Scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis is a type of scoliosis that is present at birth. It occurs when the bones in the spine do not form properly during fetal development. Congenital scoliosis is rare, affecting only about one in every 10,000 newborns. The severity of congenital scoliosis can vary, and it can be associated with other medical conditions, such as heart and kidney problems.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis
Neuromuscular scoliosis is a type of scoliosis that is caused by a medical condition that affects the nerves and muscles that control the spine. This can include conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and spina bifida. Neuromuscular scoliosis can develop at any age, and it tends to be more severe than idiopathic scoliosis.
Degenerative Scoliosis
Degenerative scoliosis is a type of scoliosis that develops in adults as a result of the natural aging process. It occurs when the discs and joints in the spine begin to degenerate, leading to a curvature of the spine. Degenerative scoliosis tends to be less severe than other types of scoliosis, but it can still cause pain and discomfort.
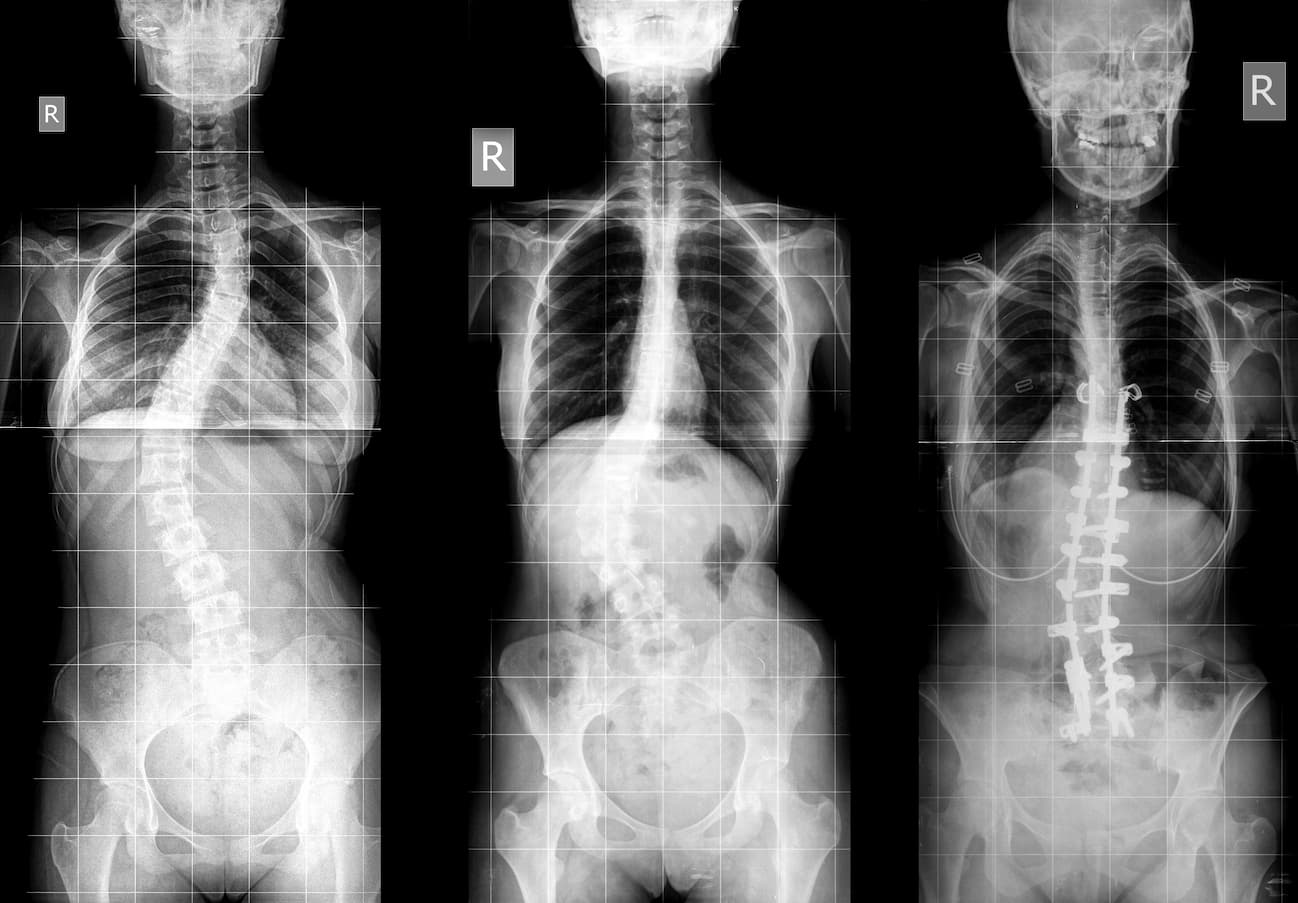
The Most Severe Type of Scoliosis
While all types of scoliosis can cause pain and discomfort, some types can be more severe than others. The most severe type of scoliosis is usually considered to be congenital scoliosis. This type of scoliosis is present at birth and is caused by abnormalities in the spine’s development. Congenital scoliosis can range from mild to severe, and the severity depends on the location and extent of the abnormality.
In some cases, congenital scoliosis can cause other complications, such as spinal cord or nerve damage, which can affect a person’s ability to move or feel sensations in certain parts of their body. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature and prevent further complications. However, with proper treatment and management, most people with congenital scoliosis can lead normal, healthy lives.
Can a Person with Scoliosis Live a Normal Life?
A person with scoliosis can live a normal life. Most cases of scoliosis are mild and do not require treatment. However, in more severe cases, treatment may be necessary to prevent the curvature from getting worse and causing pain and discomfort.
Treatment options for scoliosis can include:
Observation: for mild cases of scoliosis, observation may be the only treatment necessary.
Bracing: for moderate cases of scoliosis, a brace may be recommended to help prevent the curvature from getting worse.
Surgery: for severe cases of scoliosis, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature and prevent further progression.
With proper treatment and management, most people with scoliosis can lead normal, healthy lives. However, it’s essential to stay active and maintain good posture to prevent pain and discomfort.
What Should I Avoid If I Have Scoliosis?
If you have scoliosis, there are certain things you should avoid to prevent pain and discomfort. These include:
Heavy lifting: lifting heavy objects can strain the muscles and joints in the back, leading to pain and discomfort.
Prolonged sitting or standing: sitting or standing for long periods can put pressure on the spine, leading to pain and discomfort.
High-impact sports: high-impact sports, such as football or basketball, can put stress on the spine, increasing the risk of injury and pain.
It’s also essential to maintain good posture and exercise regularly to strengthen the muscles in the back and prevent pain and discomfort.
The Study of Types of Scoliosis
A recent study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Research examined the long-term outcomes of surgical treatment for congenital scoliosis. The study followed 150 individuals with congenital scoliosis over 10 years after undergoing spinal surgery to correct the curvature. The results of the study indicated that surgical intervention led to significant improvements in spinal alignment, pain reduction, and overall quality of life for the majority of participants. This study underscores the effectiveness of surgical treatment for congenital scoliosis in improving the lives of those affected by this type of scoliosis.
What Organs Are Affected by Scoliosis?
Severe cases of scoliosis can affect the organs in the chest and abdomen, such as the lungs, heart, and digestive system. This is because the curvature of the spine can cause compression and distortion of these organs, leading to breathing difficulties, chest pain, and digestive problems.
However, most cases of scoliosis are mild and do not cause any significant complications. With proper treatment and management, most people with scoliosis can lead normal, healthy lives.
Conclusion
Scoliosis is a medical condition that affects the curvature of the spine, leading to pain and discomfort, especially if it becomes severe. There are different types of scoliosis, including idiopathic scoliosis, congenital scoliosis, neuromuscular scoliosis, and degenerative scoliosis, each with its unique causes and characteristics. While most cases of scoliosis are mild and do not require treatment, severe cases may require treatment options such as bracing or surgery. With proper treatment and management, most people with scoliosis can lead normal, healthy lives, but it’s important to stay active, maintain good posture, and avoid activities that can cause pain and discomfort.