Symptoms of a Silent Heart Attack
Heart attacks can be a terrifying experience, and they often occur suddenly and with intense symptoms. However, not all heart attacks are the same. Some heart attacks can be silent, with subtle symptoms that may go unnoticed or dismissed as something else. This is why it’s important to understand the signs and symptoms of a silent heart attack, as they can still cause damage to your heart and even be life-threatening. In this article, we will discuss the surprising symptoms of a silent heart attack, along with some other important information you should know.
What Is a Silent Heart Attack?
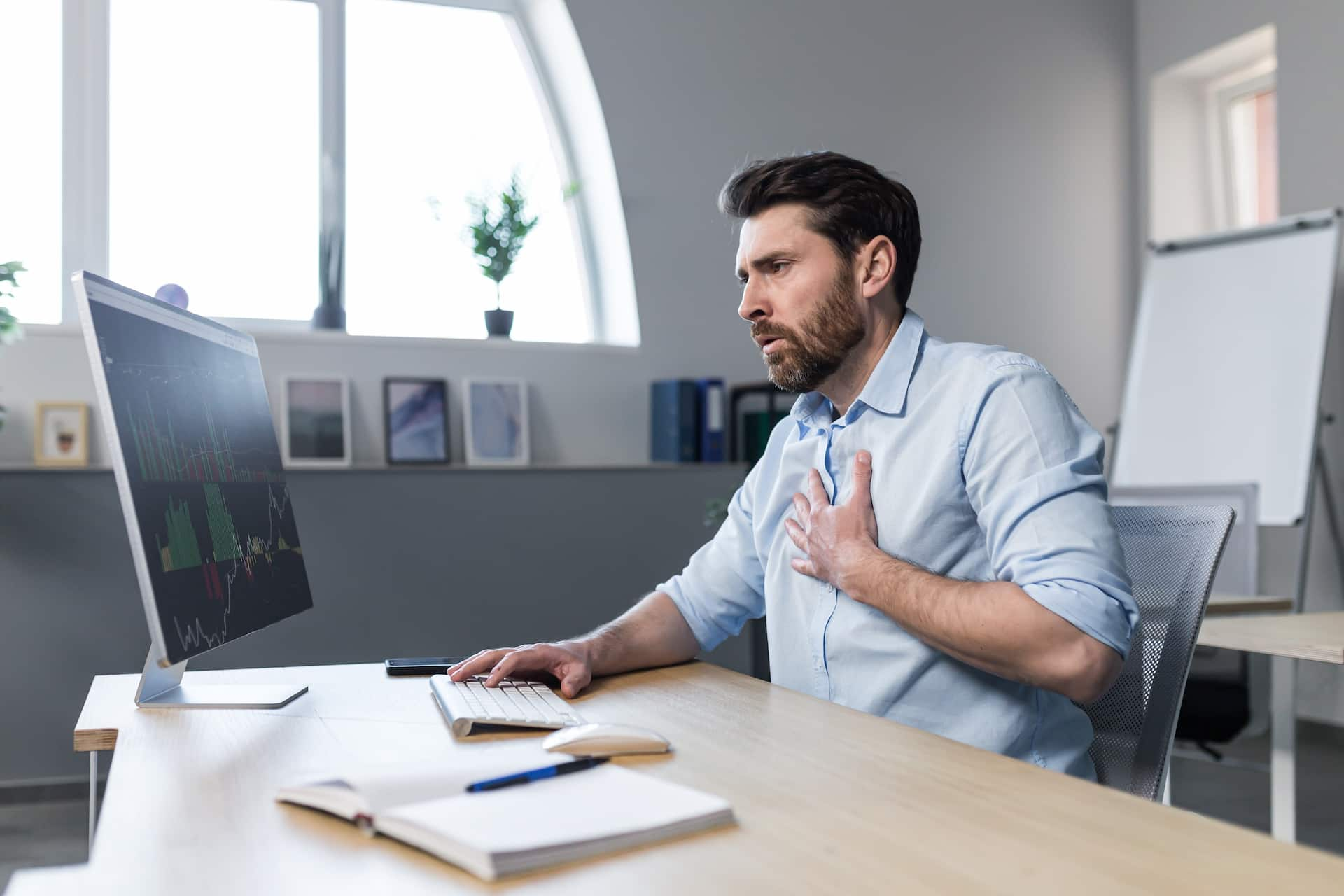
A silent heart attack is a type of heart attack that occurs without any noticeable symptoms. It is also known as a silent myocardial infarction and can be just as dangerous as a typical heart attack, causing damage to the heart muscle and even being life-threatening.
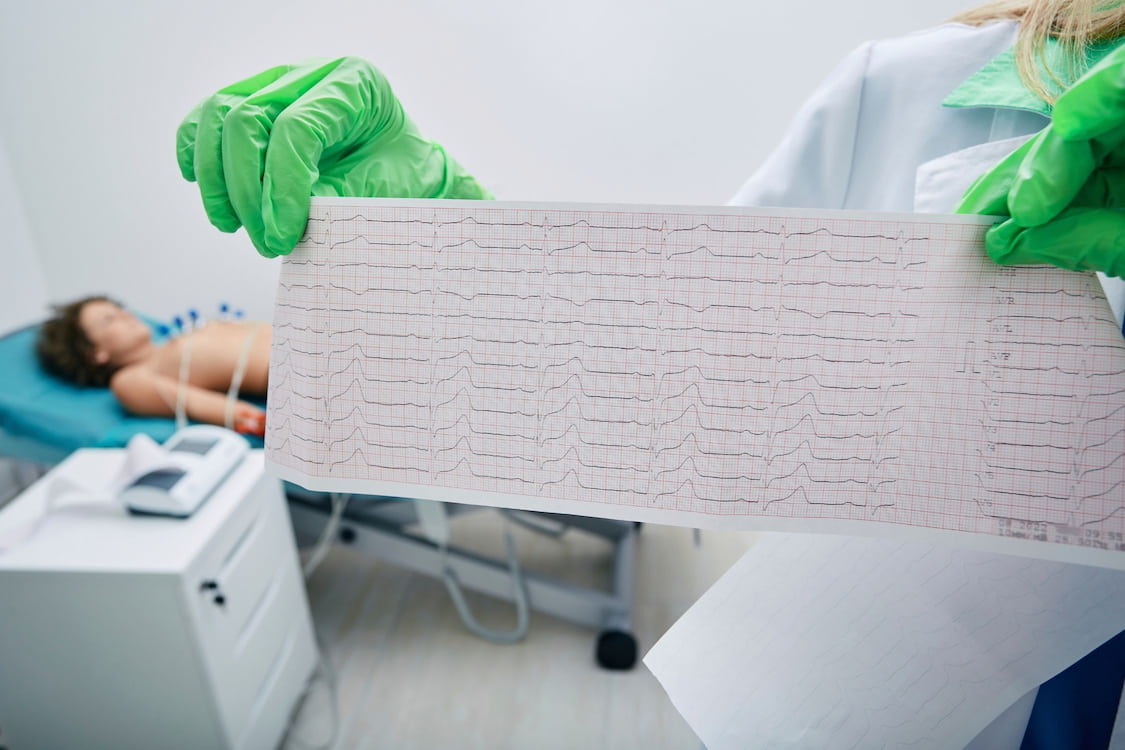
During a silent heart attack, blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked or reduced, but there are no noticeable symptoms. This can make it difficult to detect and diagnose, and it may only be discovered during a routine medical checkup or electrocardiogram (ECG). However, some people may experience mild symptoms that are similar to a typical heart attack, such as mild discomfort in the chest, arms, back, neck, or jaw, nausea or vomiting, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, dizziness or lightheadedness, and fatigue or weakness.
Risk factors for a silent heart attack include age, gender, family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and smoking. Treatment for a silent heart attack may be similar to that of a typical heart attack, depending on the severity and extent of the damage to the heart muscle. It may include medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery. By taking steps to reduce your risk of heart disease and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can help protect your heart and reduce the risk of a silent heart attack.

What Are the Warning Signs of a Silent Heart Attack?
Since silent heart attacks don’t always have obvious symptoms, it’s important to pay attention to any unusual sensations in your body. Some people may experience mild symptoms that are similar to a typical heart attack, such as:
Mild discomfort in the chest, arms, back, neck, or jaw
Nausea or vomiting
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Fatigue or weakness
These symptoms may come and go, or they may last for several minutes or hours. They may also be more noticeable during physical activity or exercise, and may go away when you rest. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away, especially if you have a history of heart disease or other risk factors.
What Are Some Uncommon Signs of Heart Attack?
In addition to the common symptoms of a heart attack, there are some other signs that may be less obvious but still important to watch out for. These include:
Cold sweats or clammy skin
Unexplained anxiety or panic attacks
Indigestion or heartburn
Flu-like symptoms, such as body aches or fatigue
Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, back, or shoulders
Unexplained feelings of fatigue or weakness
These symptoms may be more common in women, who may not always experience the typical chest pain or discomfort associated with a heart attack. It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other health issues, so it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause.
Who Is At Risk For A Silent Heart Attack?
Anyone can have a silent heart attack, but some people may be at a higher risk than others. Risk factors for a silent heart attack include:
Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age, and older adults are more likely to have a silent heart attack.
Gender: Men are more likely to have a heart attack than women, but women are more likely to have a silent heart attack.
Family history: If you have a family history of heart disease or heart attacks, you may be at a higher risk.
High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of a heart attack.
High cholesterol: High cholesterol can cause plaque buildup in the arteries, which can lead to a heart attack.
Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of a heart attack.
How Is A Silent Heart Attack Diagnosed And Treated?
A silent heart attack may be diagnosed during a routine medical checkup or electrocardiogram (ECG). If your doctor suspects that you may have had a silent heart attack, they may order additional tests, such as a stress test, echocardiogram, or angiogram. The treatment for a silent heart attack may be similar to that of a typical heart attack, depending on the severity and extent of the damage to the heart muscle. Treatment may include medications to reduce the risk of further heart damage, such as aspirin, beta-blockers, or ACE inhibitors. Lifestyle changes, such as a heart-healthy diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, may also be recommended to reduce the risk of future heart problems.
In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
The Study of Heart Attack Silent Symptoms
A recent study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association followed a cohort of 1,500 individuals aged 50 and above with various risk factors for heart disease. Over a five-year period, the study identified that 15% of participants had experienced a silent heart attack, with a startling 60% of these cases remaining undiagnosed until routine medical check-ups or incidental electrocardiograms. These findings underscore the importance of understanding the prevalence of silent heart attacks, even in individuals without obvious symptoms, and emphasize the need for increased awareness and proactive heart health management.
Conclusion
Silent heart attacks are a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can occur without any noticeable symptoms. It’s important to be aware of the warning signs and risk factors for a silent heart attack, and to seek medical attention right away if you experience any unusual sensations in your body. By taking steps to reduce your risk of heart disease and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can help protect your heart and reduce the risk of a silent heart attack.