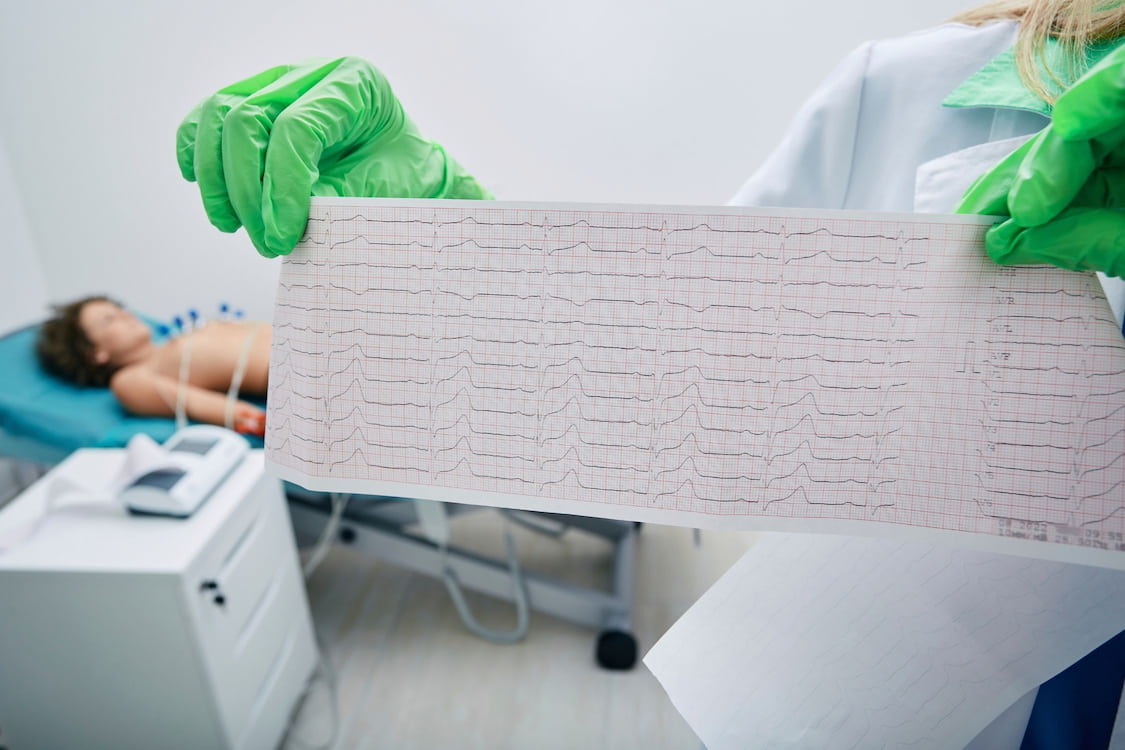
Normal Electrocardiography (ECG) Intervals
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. It records the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it contracts and relaxes, which can help identify any irregularities or abnormalities in the heart's rhythm or function. ECG is a commonly used test to diagnose various heart conditions such as arrhythmia, heart attacks, and heart failure.
ECG results can vary from person to person, depending on their age, gender, and overall health status. Therefore, understanding what is considered normal for ECG results is essential for accurate interpretation of the test.
ECG Normal Values
The normal ECG results are determined by measuring the intervals between the various electrical events that occur during a cardiac cycle. The intervals that are typically measured on an ECG are the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The P wave represents the electrical impulse that travels through the atria, while the QRS complex represents the electrical activity in the ventricles. The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
The normal values for these intervals are as follows:
P wave: < 120 ms
QRS complex: < 100 ms
QT interval: < 440 ms (for men) and < 460 ms (for women)
The PR interval, which represents the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles, should be between 120 and 200 ms.
It's important to note that these values are just general guidelines, and there may be slight variations depending on the person's age, gender, and overall health status. Therefore, it's essential to compare ECG results to the person's baseline ECG and consider their individual factors when interpreting the results.
ECG Normal Values by Age
As we age, our heart undergoes several changes, which can affect the ECG results. Therefore, it's essential to know the normal ECG values by age to accurately interpret the test results.
In children, the normal ECG values are similar to adults, with the exception of the heart rate, which is higher. In adults, the heart rate should be between 60 and 100 beats per minute, while in children, it can be as high as 150 beats per minute.
In older adults, the ECG results may show slight variations, such as a longer QT interval, which is considered normal in this age group. Therefore, it's crucial to consider the person's age when interpreting the ECG results.

ECG Normal Range for Female vs Male
Gender can also affect the ECG results, as the size and shape of the heart may differ between males and females. Therefore, it's important to know the normal ECG range for females and males to interpret the results accurately.
In general, there are no significant differences in the ECG results between females and males. However, females may have a slightly longer QT interval, which is considered normal. It's essential to compare the ECG results to the person's baseline ECG and consider their gender and individual factors when interpreting the results.
What Diseases Can Be Diagnosed with ECG?
ECG is a valuable tool in diagnosing various heart conditions, as it provides valuable information about the electrical activity of the heart. Some of the conditions that can be diagnosed with an ECG include:
Arrhythmia: An abnormal heart rhythm can be identified on an ECG by changes in the P wave, QRS complex, or T wave.
Heart attack: An ECG can help diagnose a heart attack by showing changes in the ST segment and T wave.
Heart failure: An ECG can help diagnose heart failure by showing changes in the QRS complex and T wave.
Long QT syndrome: An ECG can help diagnose long QT syndrome, a rare genetic condition that can cause sudden cardiac arrest.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: An ECG can help diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick.
In addition to these conditions, an ECG can also be used to monitor the heart's function during treatment or after surgery, and to assess the risk of future cardiac events.
Heart Rate Estimation from the ECG
One of the essential pieces of information that can be obtained from an ECG is the heart rate. The heart rate can be calculated by measuring the distance between two R waves and dividing it by the time interval between them. This calculation gives the heart rate in beats per minute (BPM).
Alternatively, one can use the 6-second strip method to estimate the heart rate. In this method, one counts the number of QRS complexes in a 6-second strip and multiplies it by ten to obtain the heart rate in BPM.
It's essential to note that the heart rate obtained from the ECG may not always be accurate, as it only provides a snapshot of the heart's electrical activity at a specific moment. Therefore, it's important to consider other factors that may affect the heart rate, such as medication, exercise, or stress, when interpreting the ECG results.
What are V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 in ECG?
The ECG records the electrical activity of the heart from twelve different angles, called leads. These leads are divided into three groups: standard limb leads, augmented limb leads, and precordial leads. The precordial leads are also known as chest leads and include V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6.
Each precordial lead records the electrical activity of the heart from a specific location on the chest. V1 and V2 are placed in the fourth intercostal space, to the right and left of the sternum, respectively. V3 is placed midway between V2 and V4, while V4 is placed in the fifth intercostal space, the midclavicular line. V5 is placed in the anterior axillary line, at the same level as V4, while V6 is placed in the midaxillary line, at the same level as V4 and V5.
The precordial leads provide valuable information about the electrical activity of the heart from different angles, which can help identify any abnormalities or irregularities in the heart's function.
Understanding ECG Result
ECG is a valuable tool in diagnosing various heart conditions, and understanding what is considered normal for ECG results is essential for accurate interpretation of the test. The normal ECG values may vary depending on the person's age, gender, and overall health status. Therefore, it's important to compare the ECG results to the person's baseline ECG and consider their individual factors when interpreting the results. Knowing the normal ECG range for females and males and understanding the role of the precordial leads can help provide a more accurate diagnosis.