Erysipelas and Cellulitis
Key Takeaways
- Erysipelas and cellulitis are bacterial skin infections caused by different bacteria and affecting different skin layers.
- Erysipelas involves superficial layers and presents with a well-defined, red, raised rash.
- Cellulitis affects deeper layers, showing diffuse redness and swelling with higher risks of complications.
- Prompt antibiotic treatment is crucial to avoid severe outcomes.
- Preventative measures include good hygiene and proper wound care.
Erysipelas and cellulitis are bacterial skin infections with overlapping symptoms but differing in causes, affected skin layers, and severity. Recognizing these differences is vital for effective treatment and prevention.
Understanding Erysipelas and Cellulitis
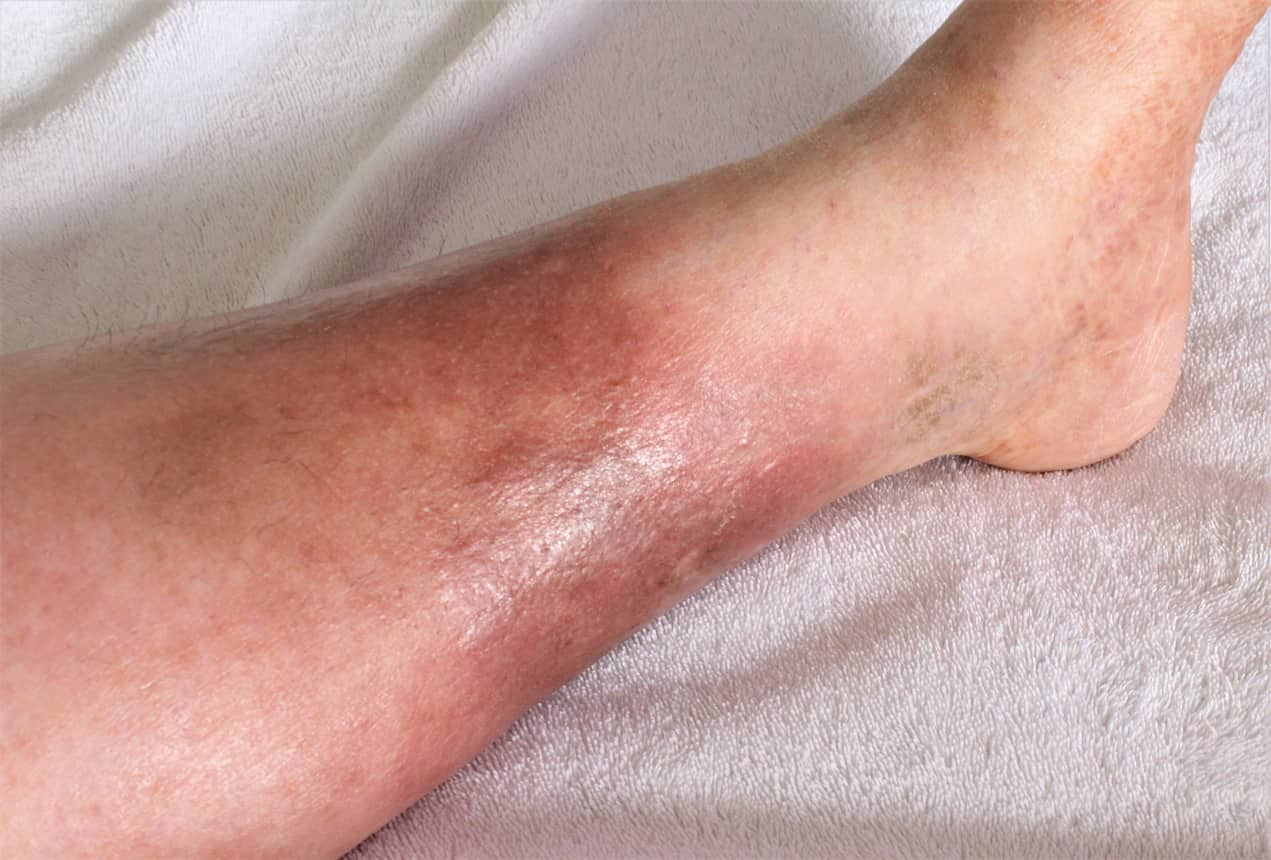
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is a superficial bacterial infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus). It typically affects the face, legs, or arms and presents as a red, raised rash with a sharp border. Symptoms include:
- Bright red, swollen, and warm skin
- Fever, chills, and fatigue
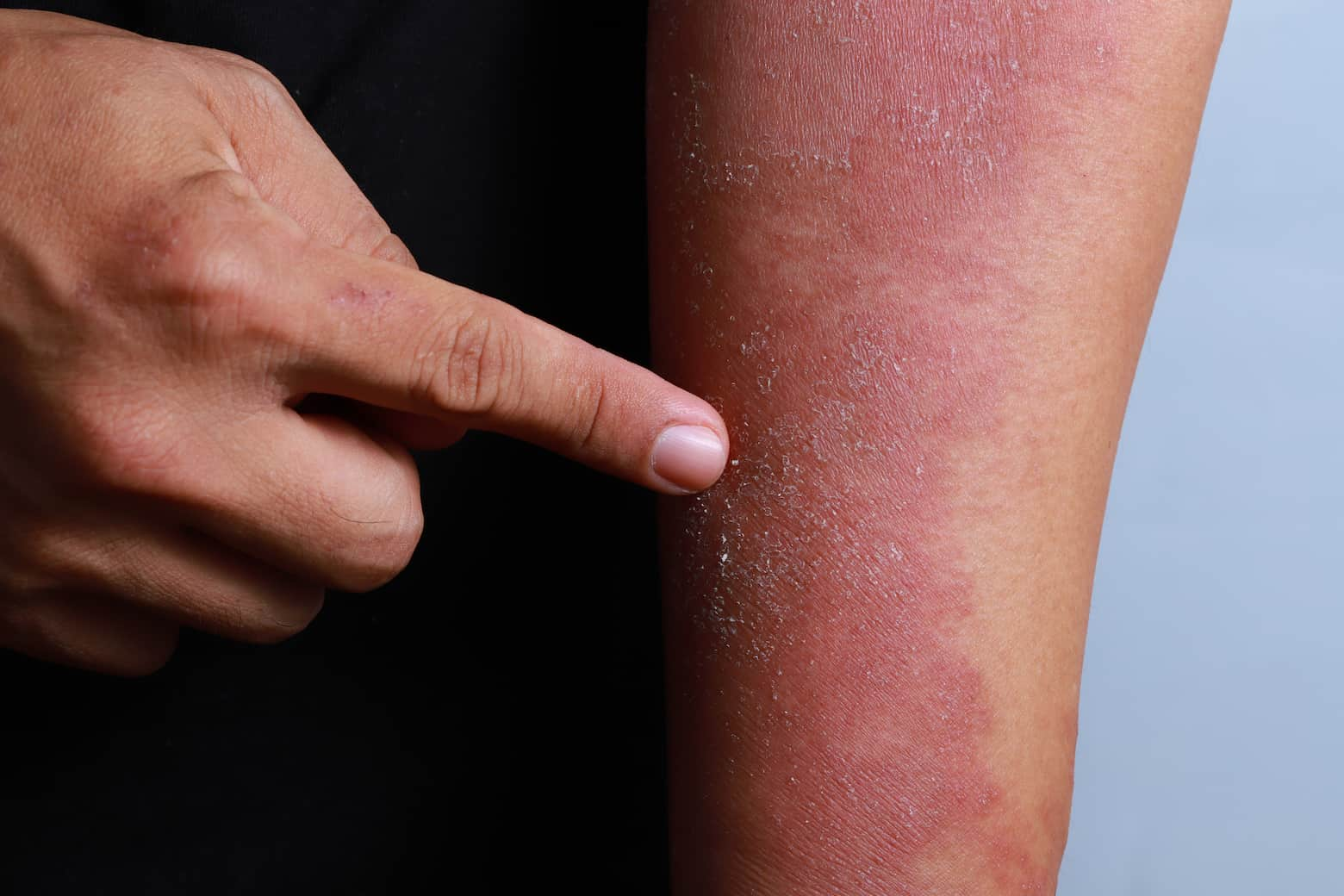
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a deeper skin infection involving subcutaneous tissues. It can be caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria and often starts as a small, tender area of redness that spreads rapidly. Symptoms include:
- Diffuse redness and swelling
- Warm, tender skin
- Fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes
Comparing Erysipelas and Cellulitis
Affected Skin Layers: Erysipelas is superficial, while cellulitis affects deeper tissues.
Appearance: Erysipelas has a well-defined border; cellulitis is more diffuse.
Severity: Cellulitis is generally more severe, with a higher risk of complications such as abscesses, sepsis, and necrotizing fasciitis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history, and possibly laboratory tests like blood cultures or skin biopsies.
Antibiotic Treatment
Erysipelas: Penicillin or cephalosporins are commonly used.
Cellulitis: Treatment may include penicillin, cephalosporins, macrolides, or clindamycin.
Severe cases might require intravenous antibiotics or hospitalization.
Supportive Measures
Rest and elevate the affected area.
Warm compresses to reduce swelling and promote drainage.
Surgery in severe cases to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue.
Prevention Tips
- Practice good hygiene and wound care.
- Clean and cover cuts or wounds promptly.
- Avoid contact with infected individuals.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
Erysipelas and cellulitis, while sharing some similarities, differ significantly in their bacterial causes, affected skin layers, and potential complications. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for effective management. Preventative measures, including proper hygiene and wound care, play a key role in reducing the risk of these infections. Stay proactive and seek prompt medical attention if symptoms arise.