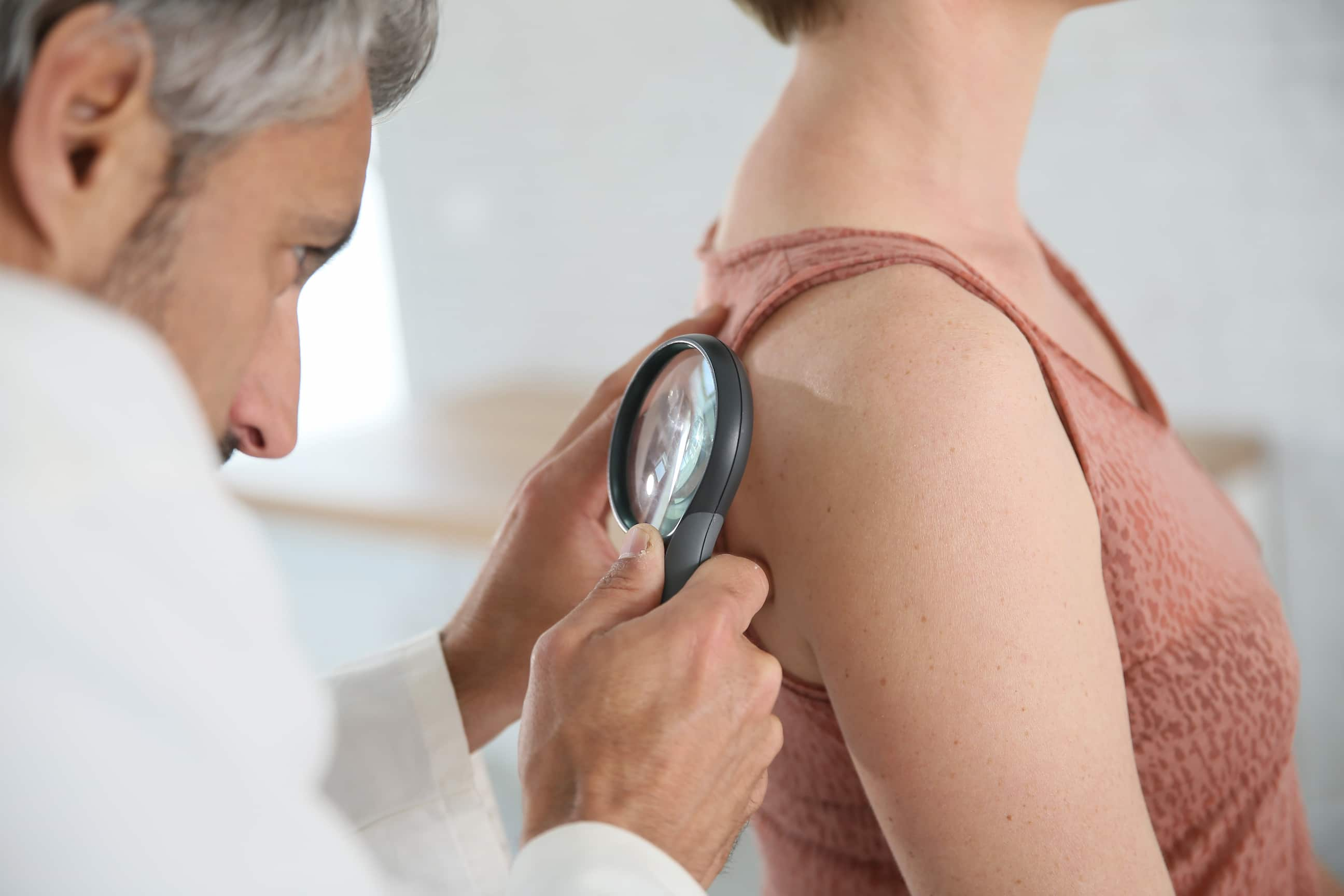
Moles and Melanomas
Moles and melanomas are two different types of skin growths, but they can sometimes look similar, making it difficult to distinguish between them. However, knowing the difference between moles and melanomas is crucial for early detection and prevention of skin cancer.
Moles, also known as nevi, are common growths on the skin. They are usually brown or black and can appear anywhere on the body. Most people have between 10 and 40 moles on their skin. Moles are generally harmless and do not require treatment, but it is important to keep an eye on them for any changes.
Melanoma, on the other hand, is a type of skin cancer that can develop from a mole or appear as a new growth on the skin. Melanoma is more dangerous than moles because it can spread quickly to other parts of the body. Early detection and treatment are critical to prevent the cancer from spreading and becoming more difficult to treat. So, how can you differentiate between moles and melanomas? Here are some key factors to consider:
Shape: Moles are typically round or oval, with smooth edges. Melanomas may have irregular or uneven edges and an asymmetrical shape.
Color: Moles are usually a uniform color, while melanomas may have multiple colors, such as shades of brown, black, or even pink, red, or white.
Size: Most moles are smaller than 6 millimeters in diameter, about the size of a pencil eraser. Melanomas can be larger and may grow over time.
Changes: Moles can change over time, but if you notice any sudden changes, such as a change in color, size, or shape, or if they become itchy, painful, or bleed, you should see a dermatologist. These changes could be a sign of melanoma.
It is important to regularly check your skin for any new growths or changes in existing moles. This can be done by performing a self-examination at home, looking for any new or changing moles, as well as any other skin changes, such as a new bump or spot.
If you are at higher risk of developing melanoma, such as having a family history of skin cancer, fair skin, or a history of sunburns, you should have a full-body skin examination by a dermatologist. This can help detect any suspicious moles or growths that may need further testing or treatment. In addition to early detection, there are steps you can take to prevent skin cancer, including:
Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and hats
Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapplying every 2 hours or after swimming or sweating
Avoiding tanning beds
In conclusion, moles and melanomas are two different types of skin growths that can sometimes look similar. Knowing the difference between the two is critical for early detection and prevention of skin cancer. Keep an eye on your moles and any changes in your skin, and practice sun safety to protect your skin from damage. If you have any concerns about your skin, see a dermatologist for a full evaluation.
How Can a Mole Be Differentiated From a Melanoma?
Before we continue, you should be aware that, regardless of the cell types involved, non-medical individuals commonly refer to a variety of dark or elevated skin lesions as “moles.” There are various kinds of skin cells, and they all serve various purposes. Ordinary moles and melanomas are caused by the melanocytes, the skin’s pigment-producing cells, overproducing too much.
Normal melanocytes make up common moles, also known as common or typical acquired nevomelanocytic nevi. In contrast, malignant melanocytes give rise to melanomas. These two dermatological disorders are the focus of the discussion that follows. You’ll see that they vary not merely in terms of outward look but also in terms of clinical history.
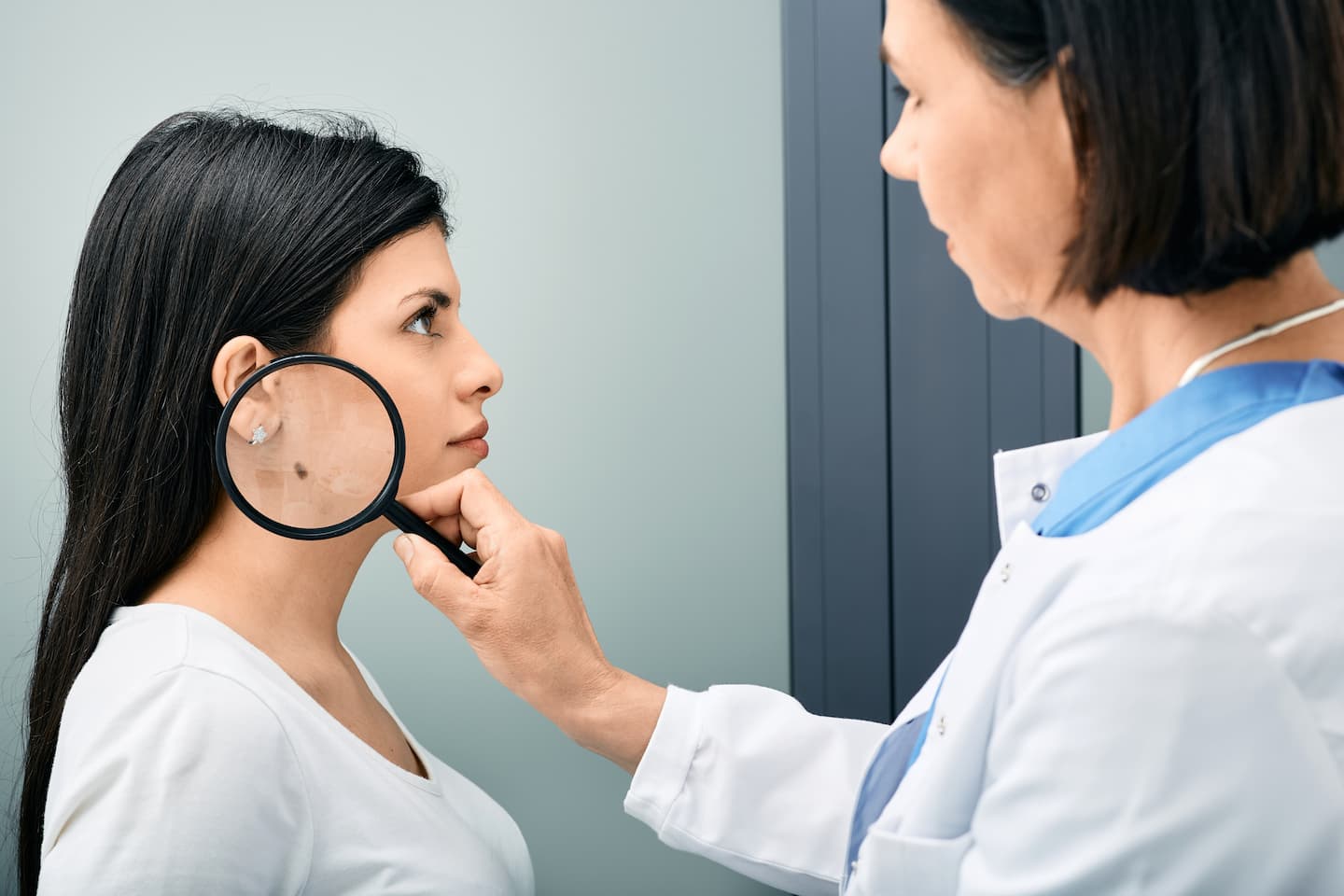
Which People Are Predisposed to Melanoma Formation?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that can develop in anyone, but there are certain factors that can increase a person’s risk of developing it. People with fair skin, light eyes, and a tendency to sunburn easily are more susceptible to developing melanoma. Those with a family history of melanoma or other types of skin cancer, as well as those with a personal history of skin cancer, are also at a higher risk.
Additionally, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds can increase the risk of melanoma formation. People who work outdoors or spend a lot of time in the sun may have an increased risk, as well as those with weakened immune systems. It is important for individuals with these risk factors to be vigilant about monitoring their skin and protecting it from sun exposure, as early detection and prevention are key in managing melanoma.
UV Radiation Extreme Exposure
Sunburns can be caused by too much sun exposure, which manifests as skin reddening or blistering that can linger for more than 12 hours. A history of sunburn as a youngster more than doubles one’s chances of developing melanoma as an adult. Sunburns raise the risk of melanoma in older people.
The use of PUVA and UVB phototherapy, as well as tanning booths, can significantly enhance melanoma susceptibility, especially when high amounts of radiation are used.
Skin Tone
Melanoma is more common in people with Fitzpatrick I and II skin phototypes than in people with Fitzpatrick III-VI skin phototypes. These individuals have light skin, red or blonde hair, and blue or green eyes. They are also more likely to have previously experienced freckles or sunburns.
The Study of Moles and Melanomas
A comprehensive study conducted by the National Cancer Institute, published in the Journal of Dermatology Research in 2020, examined the various risk factors associated with the development of melanoma. This extensive research, which analyzed data from thousands of individuals, confirmed that factors such as fair skin, a history of sunburn, and excessive UV radiation exposure significantly increase the susceptibility to melanoma. The study also underscored the importance of regular self-examinations and sun protection measures in minimizing the risk of melanoma. By highlighting these findings, we emphasize the critical role of early detection and prevention in managing melanoma and promoting skin health.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
In conclusion, moles and melanomas are two distinct types of skin growths that can sometimes look similar. While moles are generally harmless, melanoma is a serious and potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer that can develop from a mole or appear as a new growth on the skin. It is important to differentiate between the two by paying attention to factors such as shape, color, size, and changes over time. Regular self-examinations and full-body skin examinations by a dermatologist can help detect any suspicious growth and prevent the progression of melanoma. Additionally, taking steps to prevent skin damage from sun exposure, such as limiting sun exposure and using sunscreen, can reduce the risk of developing melanoma. With early detection and prevention, individuals can reduce their risk and successfully manage melanoma.