Understand Lung Cancer Stages
Lung cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer globally. The diagnosis and treatment of this disease depend on its stage, which is determined by the size of the tumor and how much it has spread. Understanding lung cancer stages is crucial for patients and their loved ones as it can provide insight into the prognosis and potential treatment options.
In this article, we will discuss the different stages of lung cancer, the symptoms associated with each stage, and the available treatment options. We will also provide tips on how to manage the side effects of treatment and cope with the emotional impact of a lung cancer diagnosis.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is broadly categorized into two types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer and accounts for around 85% of all lung cancer cases. SCLC, on the other hand, is less common and accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancer cases.
NSCLC can be further classified into different subtypes based on the type of cells that the cancer originates from. The most common subtypes of NSCLC include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma is the most common subtype of NSCLC and typically originates in the outer parts of the lungs. Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, usually starts in the lining of the bronchial tubes, while large cell carcinoma can start anywhere in the lung tissue.
SCLC, on the other hand, is typically more aggressive than NSCLC and tends to spread more quickly to other parts of the body. SCLC is usually caused by smoking and is often diagnosed at a later stage when it has already spread to other organs in the body.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is divided into four stages, ranging from stage 1 to stage 4. The stage of lung cancer is determined by the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, and whether it has metastasized (spread) to other parts of the body.
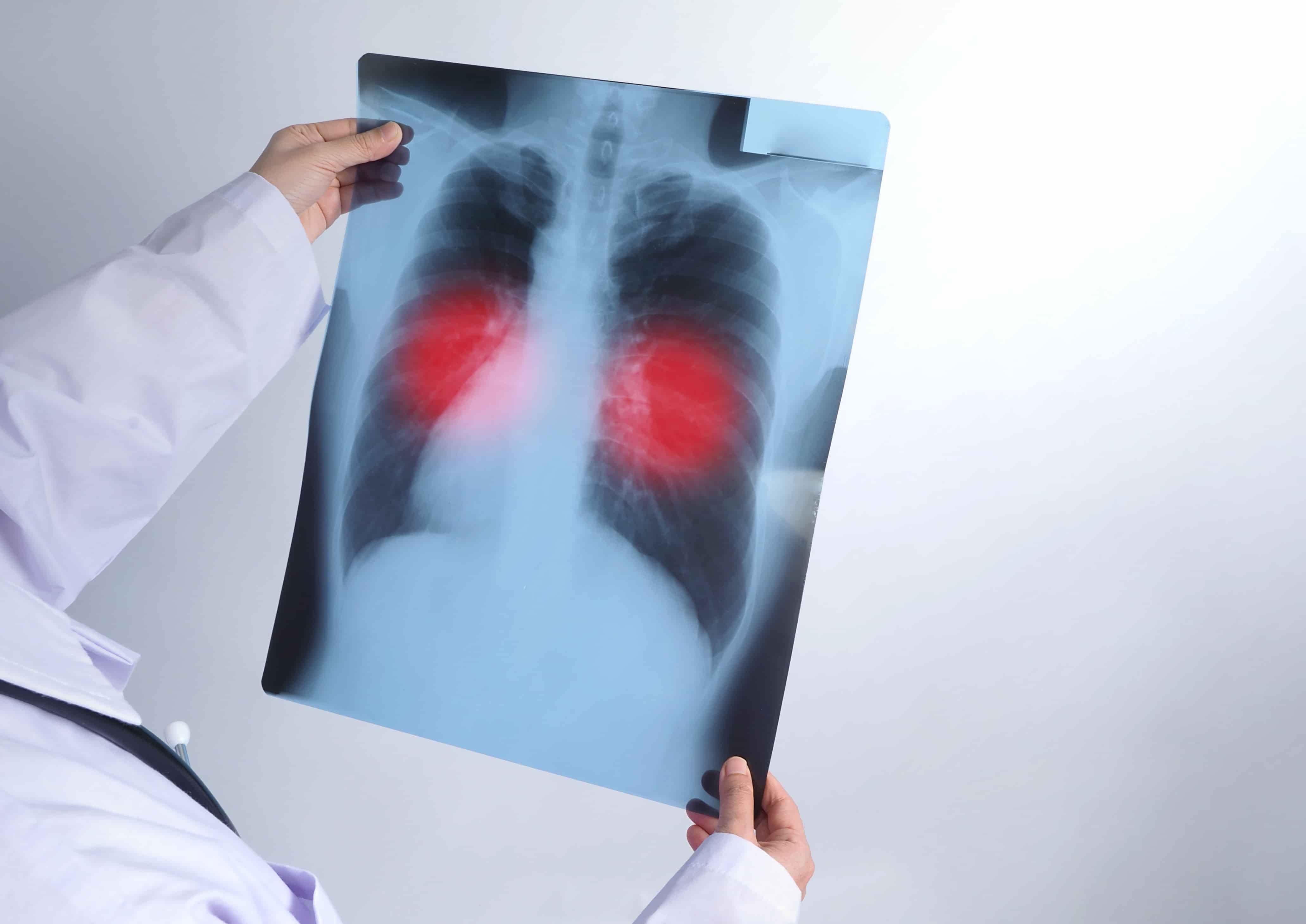
Stage 1 Lung Cancer
Stage 1 lung cancer is the earliest and most treatable stage of the disease. At this stage, the tumor is small and localized, meaning it has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Symptoms of stage 1 lung cancer may be subtle or nonexistent. Some patients may experience a persistent cough, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
Treatment for stage 1 lung cancer typically involves surgery to remove the tumor. In some cases, radiation therapy may be recommended to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Patients with stage 1 lung cancer have a good chance of a full recovery if the tumor is removed completely and they do not smoke.
Stage 2 Lung Cancer
In stage 2 lung cancer, the tumor has grown larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. Treatment for stage 2 lung cancer often involves surgery to remove the tumor and nearby lymph nodes. Radiation therapy may also be used to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
Stage 2 lung cancer is more challenging to treat than stage 1, but it is still considered a potentially curable disease. Patients with stage 2 lung cancer who receive prompt treatment have a good chance of a full recovery.
Stage 3 Lung Cancer
Stage 3 lung cancer is divided into two subcategories: stage 3A and stage 3B. In stage 3A lung cancer, the tumor has grown larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes or the chest wall. In stage 3B lung cancer, the tumor has spread to nearby tissues or organs, such as the heart, esophagus, or trachea.
Symptoms of stage 3 lung cancer may include a persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and weight loss. Treatment for stage 3 lung cancer typically involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery. Patients with stage 3 lung cancer have a lower chance of full recovery than those with stage 1 or 2 lung cancer, but some patients may still achieve long-term survival with aggressive treatment.
Stage 4 Lung Cancer
Stage 4 lung cancer is the most advanced stage of the disease, and it has spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver. Symptoms of stage 4 lung cancer may include a persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, weight loss, fatigue, and difficulty swallowing.
Treatment for stage 4 lung cancer typically involves chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy to control the spread of the disease and alleviate symptoms. Patients with stage 4 lung cancer have a lower chance of full recovery, but some patients may still achieve long-term survival with aggressive treatment.
The Study of Lung Cancer Stage
A study published in the Journal of Lung Cancer Research analyzed the treatment outcomes of 500 patients with stage 1 lung cancer. The research found that patients who underwent surgery to remove the tumor had a significantly higher survival rate compared to those who opted for other treatment modalities. The study highlighted the importance of early detection and surgical intervention in achieving favorable outcomes for stage 1 lung cancer patients.
Managing Side Effects of Lung Cancer Treatment
The treatment of lung cancer can cause several side effects, including fatigue, hair loss, nausea, vomiting, and skin irritation. These side effects can be managed with supportive care and medication.
Patients undergoing chemotherapy may experience fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. To manage these side effects, patients can take anti-nausea medication and eat small, frequent meals throughout the day. It is also important to stay hydrated and rest when needed.
Radiation therapy can cause skin irritation and fatigue. To manage skin irritation, patients can use mild soap and avoid harsh chemicals or perfumes. They should also wear loose-fitting clothing and avoid exposing the treated area to direct sunlight. Patients should also rest when needed to manage fatigue.
Coping with the Emotional Impact of Lung Cancer
A diagnosis of lung cancer can be emotionally overwhelming for patients and their loved ones. Coping with the emotional impact of the disease is an essential part of the treatment process.
Patients should seek support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals. Support groups for lung cancer patients can also provide emotional support and practical advice.
Patients should also focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as meditation or art therapy, can also help manage stress and anxiety.
Lung Cancer with Healthy Türkiye
Understanding the different stages of lung cancer is crucial for patients and their loved ones. The stage of the disease can provide insight into the prognosis and potential treatment options. Treatment for lung cancer can cause several side effects, but they can be managed with supportive care and medication.
Coping with the emotional impact of lung cancer is an essential part of the treatment process, and patients should seek support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals. By understanding lung cancer stages and managing the side effects of treatment, patients can achieve the best possible outcome and maintain a good quality of life.