Stages of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, or “man boobs,” is a condition that affects many men at some point in their lives. It occurs when there is an increase in the size of the breast tissue, resulting in a breast-like appearance. This can be a source of embarrassment for many men, as well as physical discomfort.
In this article, we’ll discuss the four stages of gynecomastia, how to identify each stage, the causes of man boobs, types of gynecomastia, how gynecomastia surgery is performed, and whether male breast reduction is permanent.
4 Stages of Gynecomastia
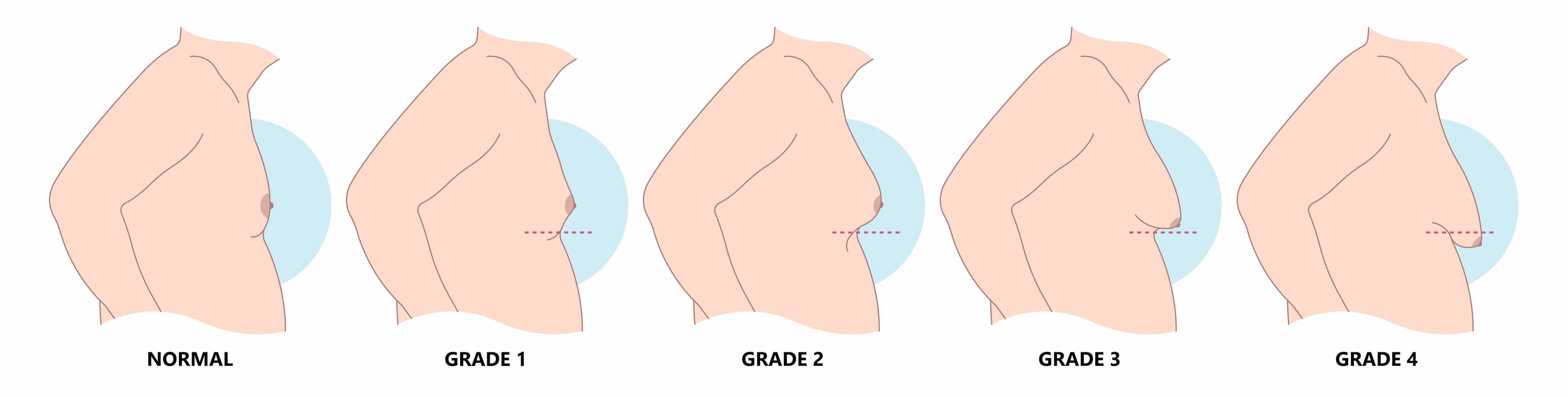
Gynecomastia is categorized into four stages, ranging from mild to severe. Each stage has its unique characteristics:
Stage 1: This is the earliest stage of gynecomastia. The breast tissue is slightly enlarged and may be felt as a small, firm lump under the nipple. This stage is usually painless and not easily visible.
Stage 2: In stage 2, the breast tissue is more enlarged, and the areola (the dark area around the nipple) becomes puffy or swollen. This stage can be uncomfortable and may cause some tenderness or sensitivity in the breast area.
Stage 3: In stage 3, the breast tissue becomes significantly enlarged, and the breast contour is more noticeable. The areola may become more prominent and may begin to sag. This stage can be very uncomfortable, both physically and emotionally.
Stage 4: Stage 4 is the most severe form of gynecomastia. The breast tissue is extremely enlarged, and the areola may be significantly larger than normal. The breasts may resemble those of a woman, with significant sagging and drooping. This stage can be very uncomfortable and may cause significant emotional distress.
How To Identify Each Stage of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can progress through different stages, and identifying the stage of gynecomastia is essential in determining the best course of treatment. Here is how to identify each stage of gynecomastia:
Stage 1: During the first stage of gynecomastia, there is a small amount of breast tissue growth around the areola. The breast tissue is not yet noticeable from a distance, and there is no excess skin. At this stage, gynecomastia is usually temporary and can resolve on its own within six months to two years.
Stage 2: In the second stage of gynecomastia, the breast tissue has started to grow, and the breast area is slightly larger than in stage 1. The breast tissue may be tender to the touch, and there may be slight pain or discomfort. At this stage, gynecomastia may still be temporary, but it may take up to two years to resolve on its own.
Stage 3: During the third stage of gynecomastia, the breast tissue has continued to grow, and the breast area is noticeably larger. There may be excess skin in the breast area, and the breast tissue may be more tender or painful. At this stage, gynecomastia is unlikely to resolve on its own and may require medical intervention.
Stage 4: In the fourth stage of gynecomastia, the breast tissue has fully developed, and the breast area is significantly larger than in the previous stages. There may be excess skin in the breast area, and the breast tissue may be very tender or painful. At this stage, gynecomastia is unlikely to resolve on its own and may require surgical intervention.
It is important to note that not all cases of gynecomastia progress through all four stages, and some cases may remain at a certain stage. If you are experiencing symptoms of gynecomastia, it is important to consult with a medical professional to determine the stage of gynecomastia and the best course of treatment.
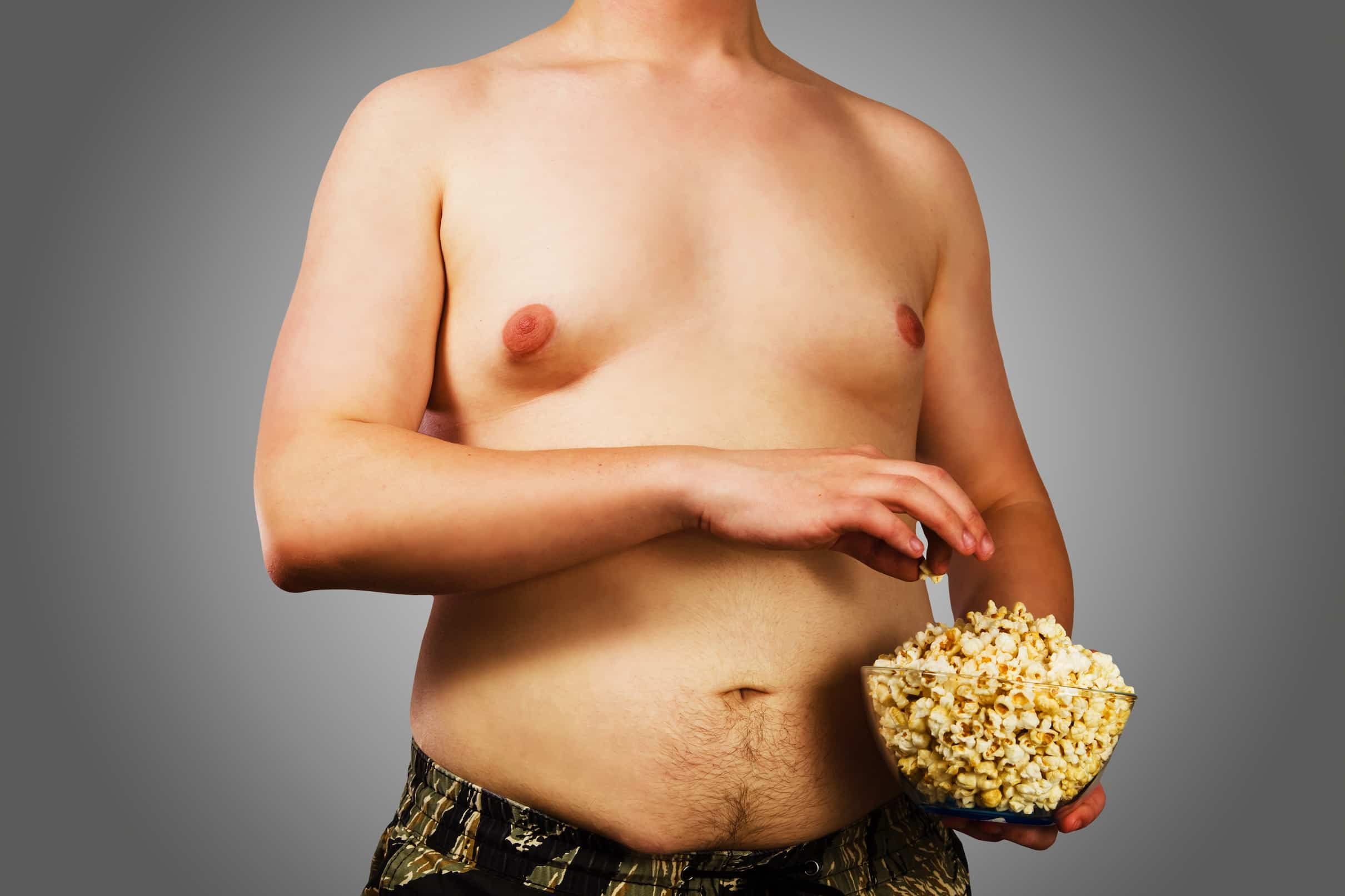

Causes of Man Boobs
There are several causes of man boobs, including hormonal imbalances, medications, and medical conditions. The most common cause of gynecomastia is a hormonal imbalance , specifically a decrease in testosterone levels or an increase in estrogen levels. This can occur during puberty, when hormone levels are fluctuating, or in older men, when testosterone levels naturally decline.
Certain medications, such as those used to treat prostate cancer , depression, or high blood pressure, can also cause gynecomastia. Medical conditions such as liver disease, kidney disease, or hypogonadism (a condition where the body does not produce enough testosterone) can also cause gynecomastia.
Types of Gynecomastia
There are two main types of gynecomastia: physiological and pathological. Physiological gynecomastia occurs during normal development in newborns, adolescents, and older men. This type of gynecomastia is usually temporary and resolves on its own. Pathological gynecomastia, on the other hand, is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication and can be more severe and long-lasting.
In addition to these two main types, there are also three subtypes of gynecomastia:
Pubertal gynecomastia: This type of gynecomastia occurs during puberty when hormone levels are fluctuating. It usually resolves on its own within a few months to a few years.
Pseudogynecomastia: This condition is not actually gynecomastia but rather an increase in fat tissue in the chest area. It can be caused by obesity or weight gain and can be improved through diet and exercise.
Asymmetrical gynecomastia: This type of gynecomastia occurs when one breast is larger than the other. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances, medications, or medical conditions and may require treatment.
The Study of Gynecomastia Stages
In a comprehensive meta-analysis involving over 1,000 male subjects, researchers conducted a systematic review of the long-term outcomes of gynecomastia surgery. The study, published in the Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, revealed that male breast reduction surgery consistently demonstrated significant and enduring results in reducing breast tissue size and improving patients’ satisfaction levels. The findings underscore the efficacy and permanence of gynecomastia surgery, providing valuable evidence for individuals considering this intervention to address physical and emotional discomfort associated with the condition.
How Gynecomastia Surgery Is Performed?
Gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, is a surgical procedure that can reduce the size of the breasts and improve their appearance. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia.
There are two main surgical techniques used for gynecomastia surgery:
Liposuction: This technique involves using a small, hollow tube (cannula) to suction out excess fat tissue from the breast area. Liposuction is typically used for cases of pseudo-gynecomastia, where the breast enlargement is due to excess fat tissue rather than breast tissue.
Excision: This technique involves removing excess breast tissue and skin through a small incision around the areola or in the natural creases of the chest. Excision is typically used for cases of true gynecomastia, where the breast enlargement is due to excess breast tissue.
After the procedure, patients will typically wear a compression garment to help reduce swelling and promote healing. Recovery time varies depending on the extent of the surgery, but most patients can return to work and normal activities within a week or two.
Is Male Breast Reduction Permanent?
Male breast reduction surgery can provide long-lasting results, but it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence. Gynecomastia surgery does not prevent future hormonal imbalances, so the condition can recur if underlying causes are not addressed. Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding medications or substances that can cause gynecomastia can help prevent a recurrence.
In conclusion, gynecomastia is a common condition that can cause physical and emotional discomfort for men. It is important to identify the stage of gynecomastia to determine the best course of treatment. Causes of man boobs can vary, but gynecomastia surgery can provide a solution for those who want to improve the appearance of their chest.
However, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent a recurrence. If you are experiencing symptoms of gynecomastia, it is important to consult with a medical professional to determine the best course of action.