Facts About Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy, also known as radiation therapy, is a common treatment for cancer. It involves the use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells or prevent them from growing. Here are 10 important facts about radiotherapy that everyone should know.
Types of Radiotherapy
There are several types of radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy. The type of radiotherapy used depends on the type and stage of cancer being treated, as well as the individual patient’s health status. Here are some of the most common types of radiation therapy:
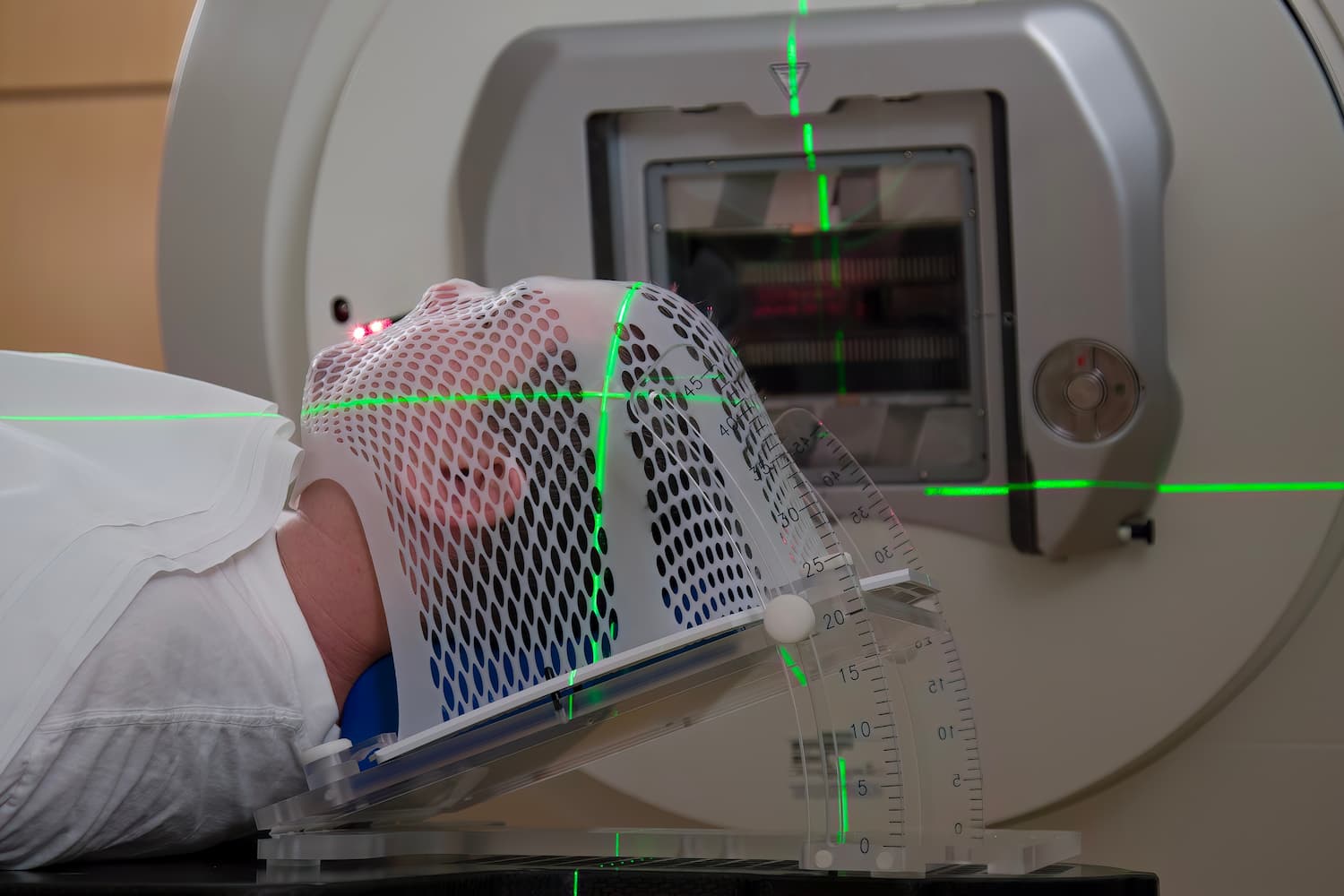
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common type of radiation therapy. It involves using a machine called a linear accelerator to deliver radiation from outside the body to the cancerous area. EBRT can be given in different doses and schedules, depending on the type of cancer being treated.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): This is a specialized type of external beam radiation therapy that uses advanced software to deliver radiation with precise and varying intensity levels. IMRT can deliver higher doses of radiation to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT): This is a type of external beam radiation therapy that uses imaging technology such as CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasound to precisely target the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): This is a specialized type of radiation therapy that delivers a highly focused, high radiation dose to a small tumor or lesion in the brain or other parts of the body. It is usually given in a single session or a few sessions.
Brachytherapy: This type of radiation therapy where radioactive sources are placed directly into or near the tumor. It can be given as a temporary or permanent implant.
Proton Therapy: This is a type of external beam radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays to deliver radiation to the tumor. Proton therapy can be more precise in targeting the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue, but it is not widely available.
Your healthcare provider will determine which type of radiation therapy is best for your specific situation.
Radiotherapy Side Effects
Radiotherapy can cause side effects, and the type and severity of side effects can vary from person to person. Some common side effects of radiotherapy include fatigue, skin changes, nausea, and diarrhea. Other side effects may include hair loss, difficulty swallowing, and a decreased appetite. Most side effects are temporary and can be managed with medication or other treatments.
Planning and Preparation
Before starting radiotherapy, you will undergo a planning and preparation process. This may involve imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans, to determine the location and size of the cancer cells. The radiation oncologist will use this information to develop a treatment plan that delivers the right amount of radiation to the cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Radiation Therapy Sessions
The number of radiation therapy sessions needed depends on the type and stage of cancer being treated, as well as the individual patient’s health status. In general, radiation therapy sessions are usually given once a day, five days a week, for several weeks.
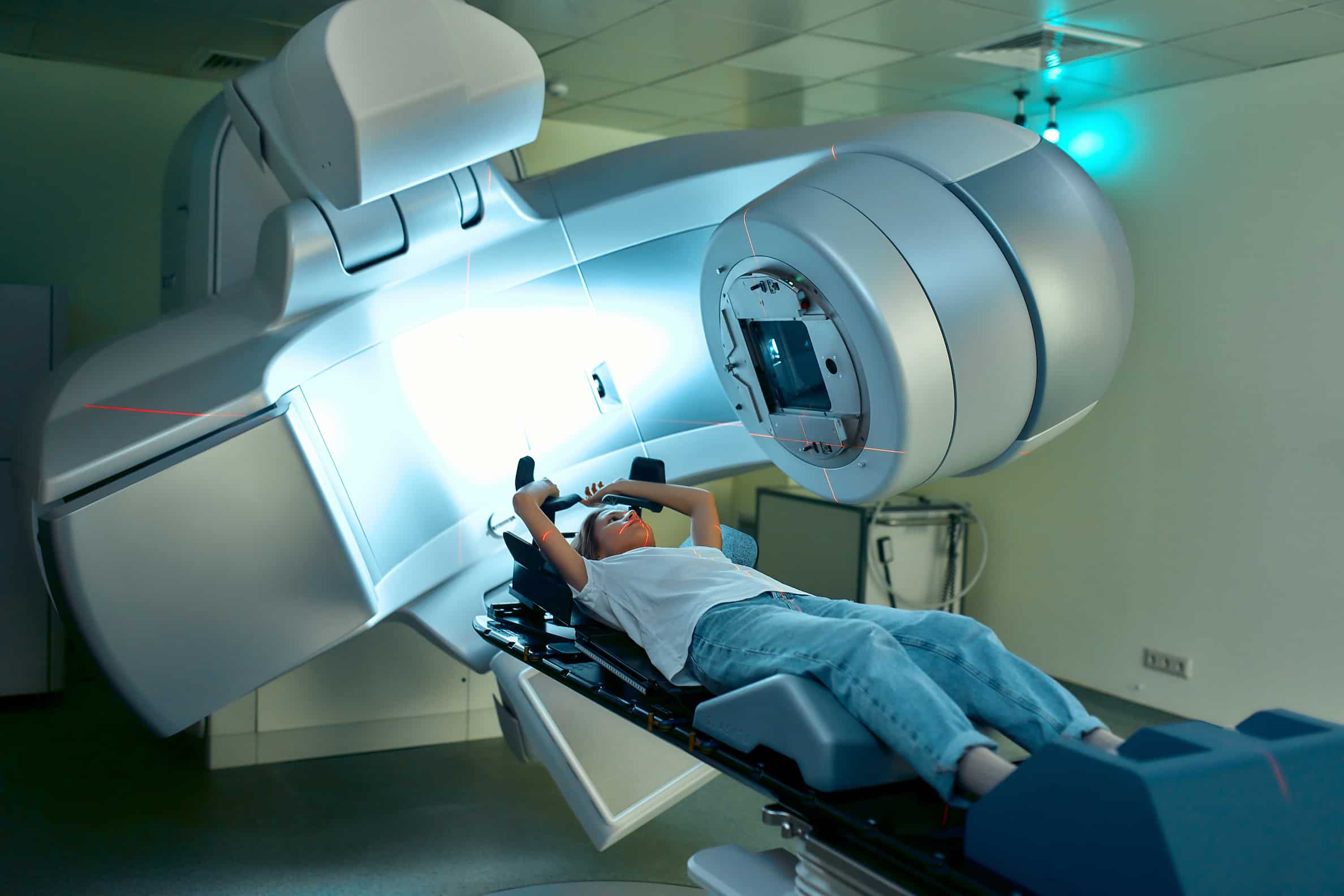
Each radiation therapy session typically lasts about 15 to 30 minutes, although the actual treatment time may only be a few minutes. The patient lies on a table while the radiation is delivered using a machine called a linear accelerator. The machine moves around the patient to deliver the radiation from different angles.
Radiation Therapy and Cancer Staging
Radiotherapy can be used to treat various types of cancer at different stages. It can be used as a standalone treatment for early-stage cancer or as part of a multimodal approach for more advanced cancer. Your cancer stage will determine the type and duration of radiotherapy treatment you receive.
Follow-Up Care
After completing radiotherapy, you will have follow-up appointments with your healthcare team to monitor your progress and manage any side effects. These appointments may include imaging tests to determine the treatment’s effectiveness and detect any new cancer growth.
Advancements in Radiotherapy
Advancements in technology have made radiotherapy more precise and effective. Newer machines can target cancer cells with greater accuracy while sparing healthy tissue. Additionally, new types of radiation, such as proton therapy, are being developed that may offer additional benefits over traditional radiotherapy.
Radiotherapy for Palliative Care
Radiotherapy can also be used for palliative care, which focuses on managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for people with advanced cancer. Palliative radiotherapy can help relieve pain and other symptoms caused by cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Costs of Radiotherapy
The cost of radiotherapy can vary depending on factors such as the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer, and the location of the treatment. In general, radiotherapy is an expensive treatment, but it is often covered by health insurance. Be sure to talk to your healthcare team and insurance provider to understand the costs associated with your treatment.
Risks of Radiotherapy
While radiotherapy is generally safe, there are some risks associated with the treatment. The most common risk is damage to healthy tissue surrounding the cancer cells being treated. This can lead to side effects such as skin irritation, fatigue, and hair loss. In rare cases, radiotherapy can cause long-term complications such as secondary cancers or damage to organs.
It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of radiotherapy with your healthcare team before starting treatment. They can help you understand the potential risks and work with you to minimize them.
The Study of Radiotherapy Facts
A recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology reviewed the outcomes of 500 cancer patients who received various forms of radiotherapy over a five-year period. The study found that advancements in radiotherapy technology have significantly improved treatment precision and effectiveness. Newer machines and techniques allowed for more accurate targeting of cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This study underscores the importance of technological advancements in enhancing the safety and efficacy of radiotherapy, providing patients with a more reliable and efficient treatment option.
Radiotherapy with Healthy Türkiye
In conclusion, radiotherapy is an important treatment option for cancer that can be used alone or in combination with other treatments. There are different types of radiotherapy, and the type of treatment you receive will depend on the type and stage of your cancer. Radiotherapy can cause side effects, but they are usually temporary and can be managed with medication or other treatments.
Before starting radiotherapy, you will undergo a planning and preparation process to develop a personalized treatment plan that delivers the right amount of radiation to the cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. After completing radiotherapy, you will have follow-up appointments with Healthy Türkiye’s healthcare team to monitor your progress and manage any side effects.
Advancements in technology have made radiotherapy more precise and effective, and new types of radiation are being developed that may offer additional benefits over traditional radiotherapy. Radiotherapy can also be used for palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life for people with advanced cancer. While radiotherapy is generally safe, there are some risks associated with the treatment, and it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare team before starting treatment.
If you or a loved one is facing a cancer diagnosis, radiotherapy may be a viable treatment option. Talk to your healthcare team to determine if radiotherapy is right for you and to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and circumstances.