Need a Pacemaker Implant
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with a heart condition, your doctor may have recommended a pacemaker implant. A pacemaker is a small device that’s implanted under the skin, usually in the chest area, to help regulate an irregular heartbeat. It’s an effective treatment option for a range of heart conditions, but how do you know if you need one? In this article, we’ll explore the signs that you may need a pacemaker, at what heart rate a pacemaker is needed, and the alternative to pacemaker treatment.
What Does a Pacemaker Do?
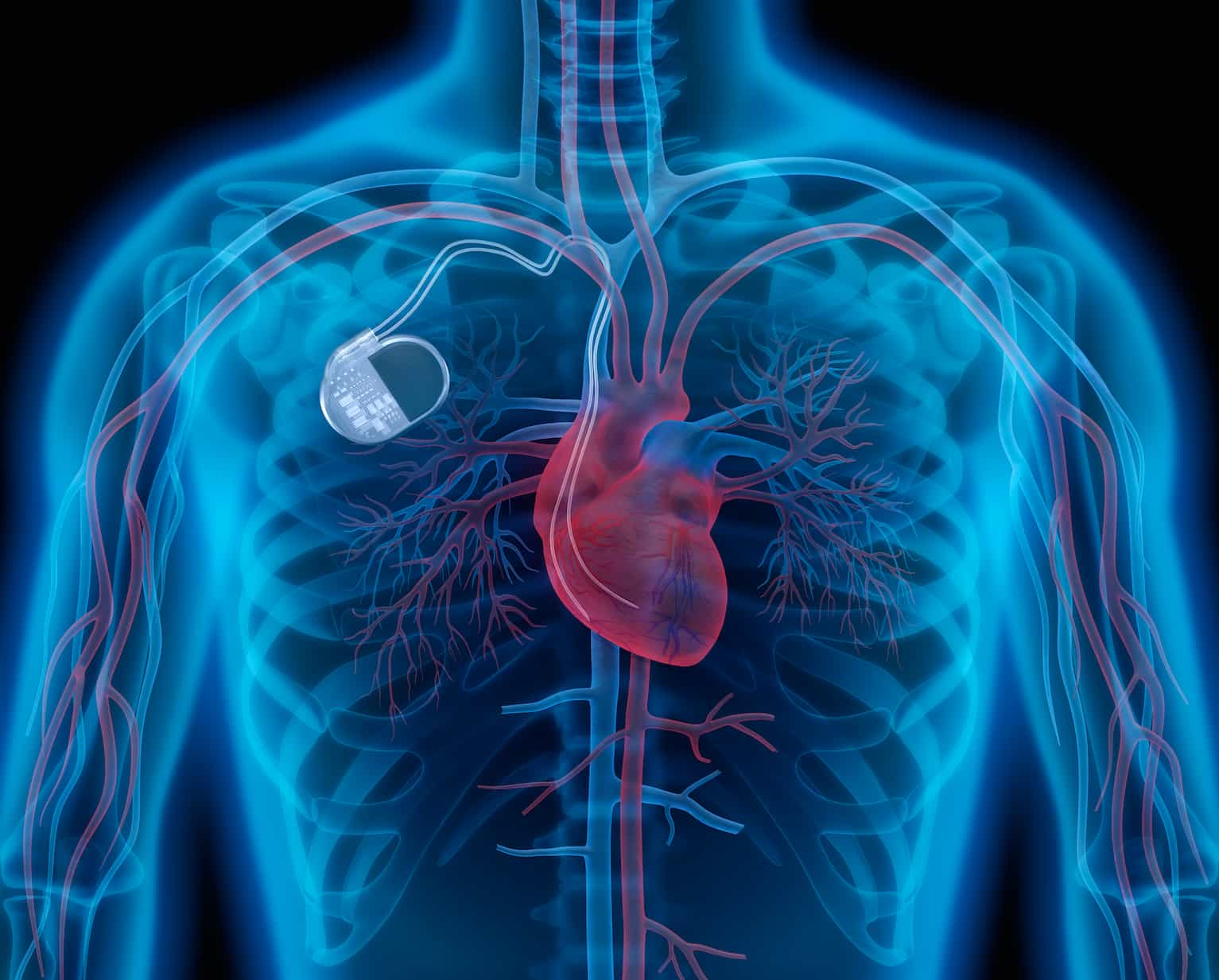
A pacemaker implant is a small device that is implanted under the skin of the chest to help regulate the heartbeat. It is used to treat heart conditions such as bradycardia, which is a slow heart rate, and heart block, which is a condition that causes the electrical signals that control the heartbeat to be disrupted.
The pacemaker implant works by sending electrical signals to the heart to help it beat at a regular pace. The device has two main components: a generator, which houses the battery and the electronic circuitry, and one or more leads, which are thin wires that are threaded through a vein into the heart. The leads are connected to the generator and transmit electrical impulses to the heart to regulate the heartbeat.
Overall, a pacemaker is an effective treatment option for people with heart conditions that cause an irregular heartbeat. It can help improve symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and fainting by regulating the heartbeat and ensuring that the heart is pumping blood effectively. Your doctor can help determine if a pacemaker implant is the right treatment option for you and can provide more information about how it works and what to expect during the implantation procedure.
When Is a Pacemaker Implant Needed?
Now that we understand what a pacemaker implant does, let’s look at the signs that you may need one. Your doctor may recommend a pacemaker if you have:
Slow heart rate: A heart rate that is slower than 60 beats per minute is known as bradycardia. Symptoms of bradycardia can include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fainting. If you have bradycardia, your doctor may recommend a pacemaker to help regulate your heart rate.
Heart block: Heart block is a condition in which the electrical signals that control the heartbeat are delayed or blocked. This can lead to a slow or irregular heartbeat, which can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, and fainting. A pacemaker can help regulate the heartbeat and prevent these symptoms.
Cardiac arrest: If you have had a cardiac arrest, which is when the heart suddenly stops beating, your doctor may recommend a pacemaker to help regulate your heartbeat and prevent future episodes.
Heart failure: In some cases, heart failure can lead to an irregular heartbeat. A pacemaker can help regulate the heartbeat and improve the symptoms of heart failure.

What Heart Conditions Require a Pacemaker Implant?
There are several heart conditions that may require a pacemaker implant. Some of the most common conditions include:
Atrioventricular block: This is a condition in which the electrical signals that control the heartbeat are delayed or blocked between the atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart.
Sick sinus syndrome: This is a condition in which the heart’s natural pacemaker (sinus node) is not functioning properly, leading to an irregular heartbeat.
Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome: This is a condition in which the heart alternates between a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) and a fast heartbeat (tachycardia).
What Heart Rate Is a Pacemaker Implant Needed?
A pacemaker implant may be needed if your heart rate is too slow, usually less than 60 beats per minute. However, the decision to implant a pacemaker is based on more than just the heart rate. Your doctor will take into account your overall health, symptoms, and medical history when making a recommendation.
What Is The Alternative To Pacemaker Treatment?
If you have a heart condition that requires a pacemaker, there may be alternative treatments available. These may include medications, lifestyle changes, or other medical procedures such as cardiac ablation, which is a procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to destroy abnormal heart tissue that is causing an irregular heartbeat. Your doctor will discuss the different treatment options with you and recommend the most appropriate one based on your specific situation.
What Is the Life Expectancy of a Person With a Pacemaker?
The life expectancy of a person with a pacemaker is typically the same as that of someone without a pacemaker. However, the lifespan of the pacemaker itself can vary depending on the type and brand. Most pacemakers last between 5 and 15 years, although some can last up to 25 years. Your doctor will monitor your pacemaker regularly to ensure that it is functioning properly and will recommend a replacement when necessary.
The Study of Pacemaker
In a recent study published in the Journal of Cardiac Electrophysiology, researchers conducted a comprehensive analysis of patients who received pacemakers to regulate their heartbeats. The study aimed to determine the effectiveness of pacemakers in improving the symptoms associated with irregular heartbeats. The research included a diverse group of individuals with various heart conditions that required pacemaker implantation. Findings from the study showed that pacemakers were particularly effective in alleviating symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and fainting, which are often associated with bradycardia, heart block, and other irregular heartbeat conditions. The study’s results underscored the importance of pacemakers as a valuable treatment option for individuals with specific heart conditions, significantly enhancing their quality of life.
Do You Feel Better After a Pacemaker Implant?
If you need a pacemaker, you may be wondering if it will make you feel better. The answer is that it depends on your specific situation. If you have been experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or fainting due to an irregular heartbeat, a pacemaker can help regulate your heartbeat and improve these symptoms. However, if your symptoms are caused by other factors, a pacemaker may not make a significant difference.
Can Your Heart Still Stop With a Pacemaker?
While a pacemaker can help regulate an irregular heartbeat, it does not prevent the heart from stopping altogether. If you experience a cardiac arrest, a pacemaker will not be able to restart your heart. In this case, you will need to receive prompt medical attention, including CPR and defibrillation, to help restore your heartbeat.
In conclusion, if you have been diagnosed with a heart condition, your doctor may recommend a pacemaker to help regulate your heartbeat. Signs that you may need a pacemaker include a slow heart rate, heart block, cardiac arrest, or heart failure. Pacemakers can also be used to treat conditions such as atrioventricular block, sick sinus syndrome, and bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome. While a pacemaker can help improve symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and fainting, it does not prevent the heart from stopping altogether. Your doctor at Healthy Türkiye will recommend the most appropriate treatment option based on your specific situation and will monitor your pacemaker regularly to ensure that it is functioning properly.