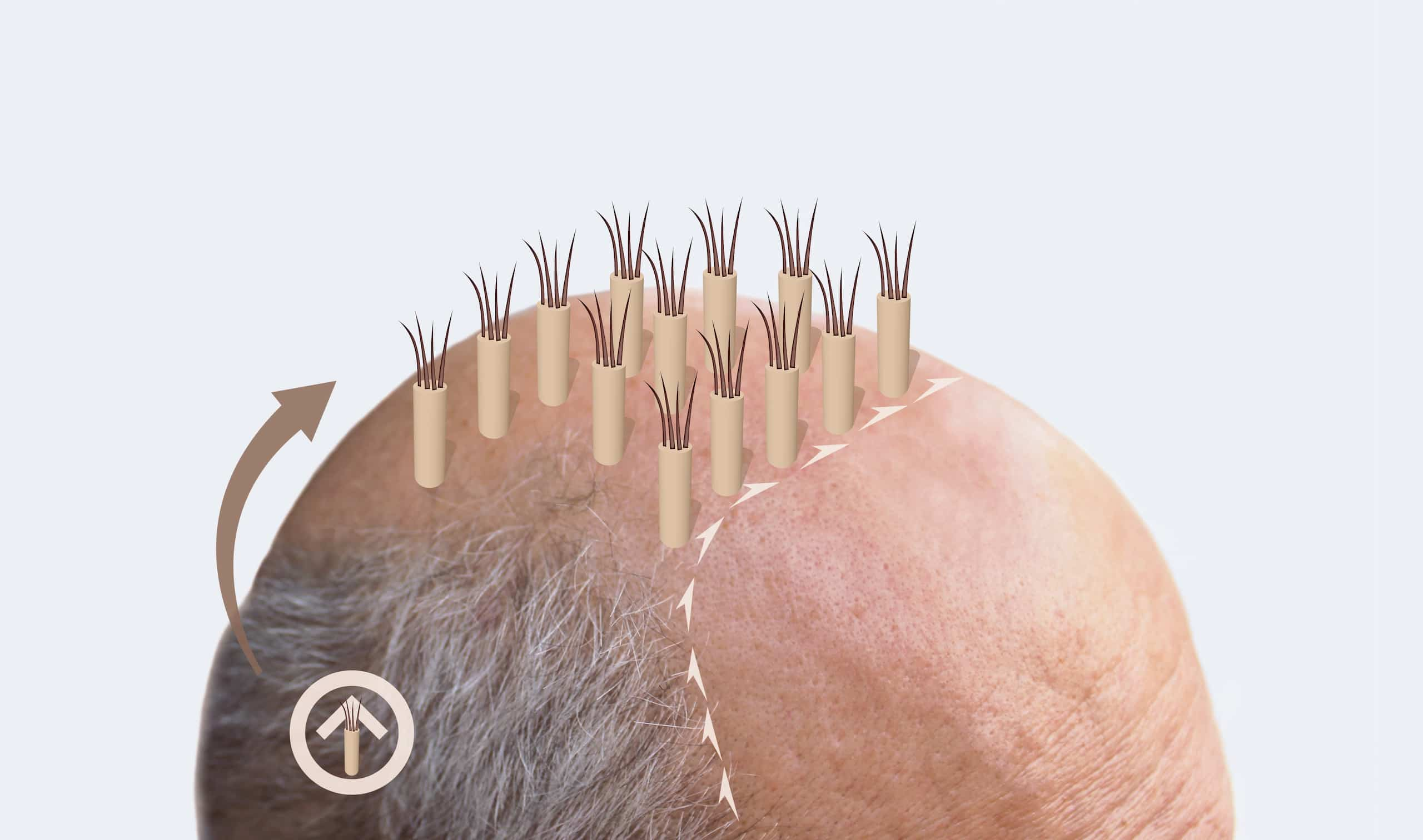
The Science Behind FUT Hair Transplant: Understanding the Procedure
Follicular Unit Transplantation, commonly known as FUT, is a surgical hair restoration procedure that has been gaining popularity in recent years. This technique involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area of the scalp, typically from the back of the head, and then dissecting it into small grafts containing hair follicles. These grafts are then transplanted into the balding or thinning areas of the scalp, where they will continue to grow hair naturally.
But what is the science behind FUT hair transplant? How does it work, and why is it considered one of the most effective hair restoration procedures available today? In this article, we will delve into the technical aspects of FUT hair transplant, and explore the underlying science that makes it possible.
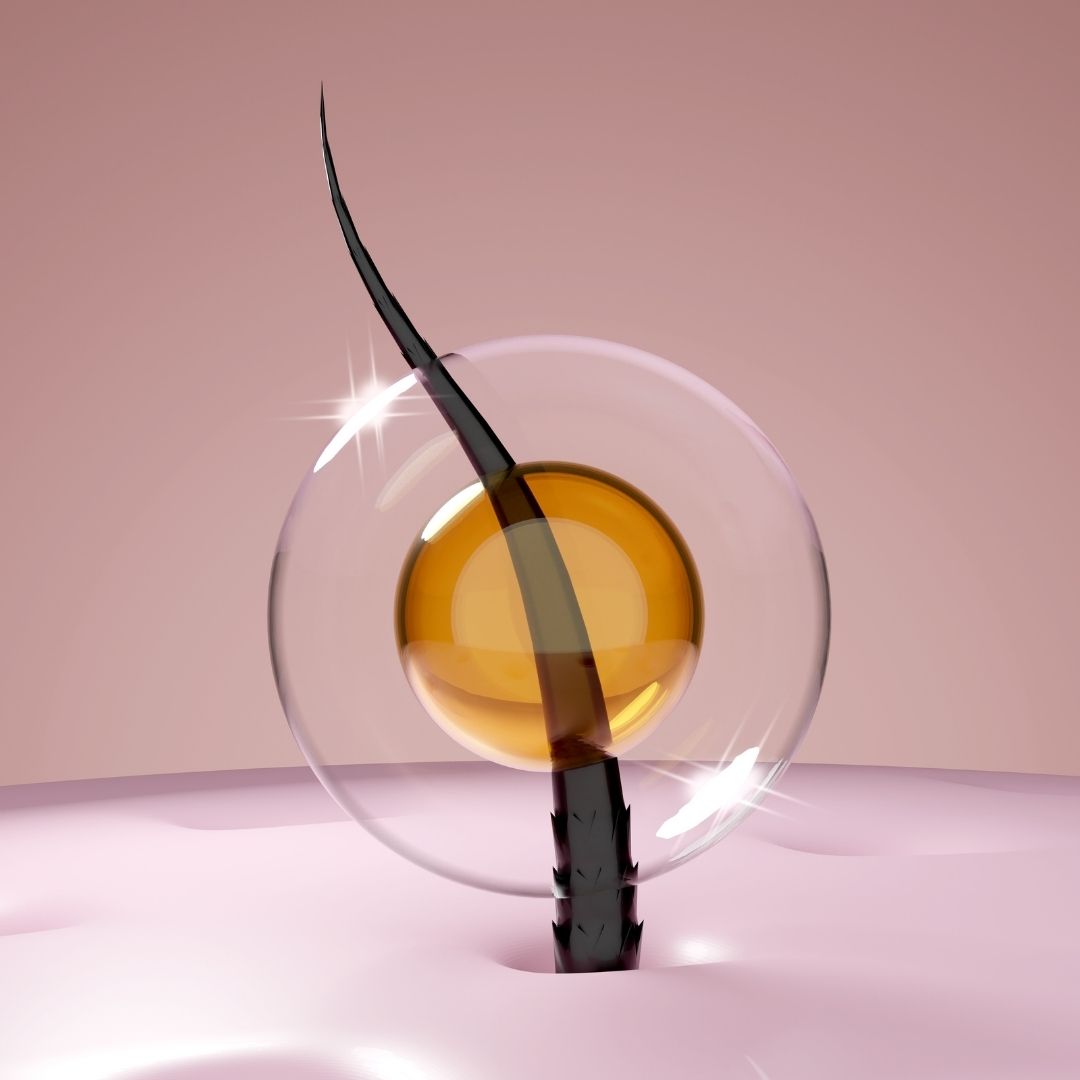
Firstly, it is important to understand that hair growth is controlled by hair follicles, which are tiny structures located in the skin. Each hair follicle contains a group of cells that work together to produce a hair shaft, which grows out of the follicle and eventually falls out. However, the follicle remains alive and active and will produce a new hair shaft in its place.
In a healthy scalp, hair follicles are evenly distributed, with each follicle containing one or more hairs. However, in people with male or female pattern baldness, hair follicles in certain areas of the scalp become miniaturized and stop producing hair altogether. This is due to a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and can result in a visible bald spot or thinning hair.
This is where FUT hair transplant comes in. By transplanting healthy hair follicles from the donor area of the scalp to the balding or thinning areas, FUT can restore hair growth and improve the overall appearance of the scalp. But how does the procedure work in detail?
FUT Hair Transplant Steps
The following procedures are commonly included in FUT hair transplantation:
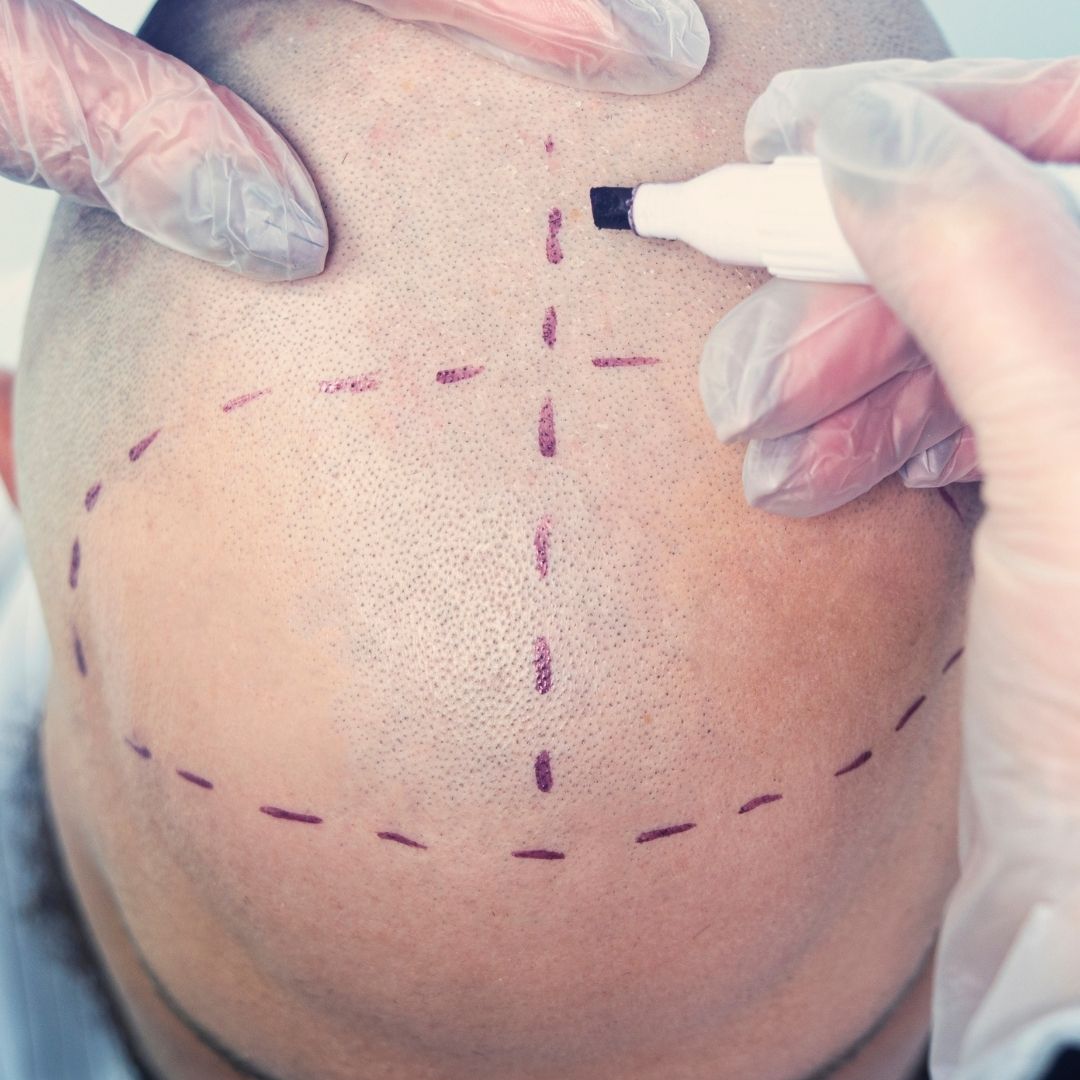
Preoperative planning: The surgeon will examine the patient's scalp and determine the best location for the donor area. This area is typically located at the back of the head, where hair is more resistant to balding.
Local anesthesia: The patient will receive local anesthesia to numb the scalp and reduce any discomfort during the procedure.
Donor area removal: The surgeon will use a scalpel to remove a strip of skin from the donor area. This strip is typically 1-2 cm wide and 10-20 cm long, depending on the number of grafts needed.
Graft dissection: The strip of skin is then dissected into small grafts, each containing 1-4 hair follicles. This is done under a microscope to ensure that each graft is of the highest quality.
Recipient area preparation: The surgeon will prepare the recipient area of the scalp by creating tiny incisions or slits where the grafts will be placed.
Graft placement: The grafts are then carefully placed into the recipient area, one by one, using forceps or a special implanting tool. The surgeon will ensure that each graft is placed at the correct angle and depth, to ensure a natural-looking result.
Postoperative care: The patient will receive instructions on how to care for the scalp after the procedure, and will be advised to avoid strenuous activities and direct sunlight for several days.
The science behind FUT hair transplant lies in the ability of hair follicles to regenerate and produce new hair growth. By transplanting healthy hair follicles from the donor area to the recipient area, FUT can stimulate new hair growth and restore the natural appearance of the scalp. The procedure is highly technical and requires a skilled surgeon with expertise in hair restoration, but when performed correctly, it can produce excellent results that can last a lifetime.
FUT Hair Transplant Recovery
Recovering from a FUT hair transplant typically takes several weeks, and patients need to follow their surgeon's postoperative instructions carefully to ensure the best possible outcome. During the first few days after the procedure, patients may experience some pain, swelling, and redness around the donor and recipient areas, which can be managed with pain medication and cold compresses. Patients will also need to avoid strenuous activities and direct sunlight during this time. In the weeks following the procedure, patients may notice some shedding of the transplanted hair, which is normal and temporary. However, within a few months, new hair growth should start to become visible. Patients need to attend all follow-up appointments with their surgeon to monitor their progress and address any concerns. With proper care and patience, FUT hair transplant recovery can be a smooth and successful process.
What Should You Avoid During Your FUT Hair Transplant Recovery
During FUT hair transplant recovery, it is important to avoid certain activities that can disrupt the healing process and jeopardize the success of the procedure. Patients should avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, as these habits can impede the body's natural healing mechanisms and increase the risk of infection. Strenuous physical activities, including exercise and heavy lifting, should also be avoided for at least two weeks to prevent bleeding and strain on the scalp.
Patients should also avoid exposure to direct sunlight and heat, as this can cause irritation and damage to the scalp. It is important to follow all postoperative instructions provided by the surgeon, including proper cleaning and care of the scalp and avoiding tight hats or helmets that can put pressure on the transplanted area. By following these guidelines, patients can ensure a smooth and successful recovery from FUT hair transplant.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
In conclusion, FUT hair transplant is one of the most effective hair restoration procedures available today, thanks to its ability to utilize healthy hair follicles from the donor area and transplant them to the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. By understanding the underlying science behind FUT hair transplant, patients can gain a better appreciation of how the procedure works and what to expect during the process.
It is important to note that FUT hair transplant is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and not all patients may be suitable candidates for the procedure. Patients must have enough healthy hair in the donor area to supply the required number of grafts and must have realistic expectations of the results.
Additionally, like all surgical procedures, FUT hair transplant carries some risks, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring. However, these risks can be minimized by choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon and following postoperative instructions carefully.
Overall, FUT hair transplant is a safe and effective hair restoration option that can improve the appearance of the scalp and boost self-confidence. By understanding the science behind the procedure, patients can make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey and achieve the best possible results.
.jpg)
.jpg)