Is Endoscopy Painful?
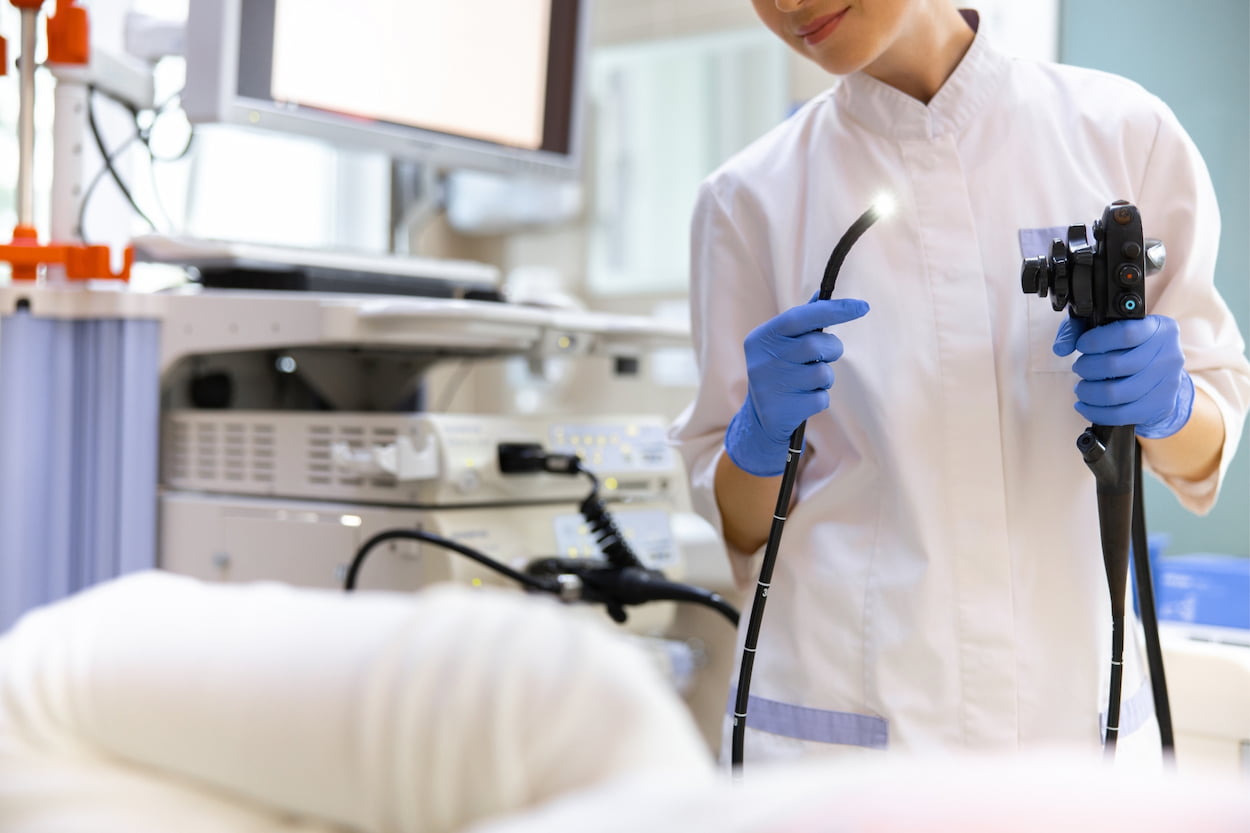
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that is used to examine the inside of the body. It involves the insertion of a flexible tube, known as an endoscope, through a natural opening, such as the mouth or rectum. Endoscopes are equipped with a light and a camera, which allow doctors to view the internal organs and tissues on a monitor. Endoscopy is commonly used to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory problems, and urological issues.
What is Endoscopy?
Endoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that enables doctors to visualize the internal organs and tissues of the body without invasive surgery. It is a non-surgical method that involves the use of a flexible tube called an endoscope, which is inserted through a natural opening in the body, such as the mouth or rectum. The endoscope is equipped with a light and a camera, which enables the doctor to view the inside of the body on a monitor.
What Diseases Can Be Detected By An Endoscopy?
Endoscopy is a versatile medical procedure that can be used to detect a variety of diseases and conditions affecting different parts of the body. Some of the most common medical conditions that can be detected by endoscopy include:
Gastrointestinal diseases: Endoscopy is frequently used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the digestive system. This includes conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcers, tumors, and polyps. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (EGD) can be used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, while lower gastrointestinal endoscopy (colonoscopy) can be used to examine the colon and rectum.
Respiratory diseases: Endoscopy can be used to diagnose and treat respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, and asthma. Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic procedure that allows doctors to examine the airways and lungs, and to collect tissue samples for further analysis.
Ear, nose, and throat (ENT) diseases: Endoscopy can be used to examine the ear, nose, and throat and to diagnose and treat conditions such as chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, and tumors. This can be done with nasopharyngoscopy, which involves inserting a thin, flexible endoscope through the nose to examine the upper airway and throat.
Gynecological diseases: Endoscopy can be used to diagnose and treat gynecological conditions such as uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, and endometriosis. Laparoscopy is an endoscopic procedure that allows doctors to examine the pelvic area and perform minimally invasive surgery.
Urological diseases: Endoscopy can be used to diagnose and treat urological conditions such as kidney stones, bladder tumors, and prostate cancer. Cystoscopy is an endoscopic procedure that allows doctors to examine the bladder and urethra and to perform minimally invasive surgery.
Overall, endoscopy is a useful diagnostic tool that can be used to detect a variety of medical conditions affecting different parts of the body. If you are experiencing symptoms related to any of the above-mentioned conditions, you should talk to your doctor about whether endoscopy is an appropriate diagnostic and treatment option for you.
Is Endoscopy Painful Without Sedation?
Endoscopy is generally considered to be a non-painful procedure. However, some patients may experience discomfort or mild pain during the procedure. The level of discomfort or pain may depend on several factors, such as the type of endoscopy, the individual's pain tolerance, and the doctor's technique.
Without sedation, endoscopy can be an uncomfortable experience for some patients. During the procedure, the endoscope is inserted through the mouth, nose, or anus and advanced through the digestive or respiratory tract. This can cause a sensation of pressure, discomfort, or mild pain. Patients may also experience gagging, coughing, or a feeling of fullness in the stomach or intestine.
The level of discomfort or pain may be greater in certain types of endoscopy procedures. For example, bronchoscopy (endoscopy of the lungs) can be particularly uncomfortable, as the endoscope is passed through the nose or mouth and down the windpipe. Similarly, ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) can be a more invasive and uncomfortable procedure, as it involves passing an endoscope through the mouth and into the small intestine to examine the bile ducts.
However, it's important to note that discomfort or mild pain during endoscopy is usually temporary and typically subsides once the procedure is complete. Some patients may experience a sore throat or mild abdominal discomfort after the procedure, but these symptoms generally go away within a few hours.
Endoscopy with Sedation
Patients who are anxious or uncomfortable during the endoscopy procedure may be offered sedation to help them relax. Sedation can be administered in several ways, including through an injection, a nasal spray, or a tablet. Sedation can help patients feel more comfortable during the procedure, but it may also cause drowsiness and impair their ability to drive or operate machinery for several hours after the procedure.
Endoscopy Side Effects
Endoscopy is generally a safe procedure, but there are some potential side effects that patients should be aware of. Some patients may experience a sore throat or hoarseness after the procedure, which should resolve within a few days. Rarely, patients may experience bleeding, infection, or damage to the internal organs. Patients who experience severe pain, bleeding, or difficulty breathing after the procedure should seek medical attention immediately.
Another potential side effect of endoscopy is the reaction to sedation. Patients who receive sedation may experience drowsiness, dizziness, or nausea after the procedure. They may also experience a headache, muscle aches, or a dry mouth. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few hours.
How Long Does An Endoscopy Take?
The duration of an endoscopy procedure can vary depending on the type of endoscopy and the reason for the examination. Most endoscopy procedures take between 20 to 60 minutes to complete. However, more complex procedures such as ERCP or endoscopic ultrasound may take longer. Patients should expect to spend some time in the recovery room after the procedure to allow the sedation to wear off.
How To Avoid Gagging During Endoscopy
Gagging is a common problem during endoscopy, but several techniques can be used to minimize the discomfort. Patients can try to breathe deeply and slowly through the nose, which can help to reduce the sensation of gagging. They can also focus on a point on the ceiling or a wall to help distract them from the procedure. Some patients find it helpful to swallow before the endoscope is inserted to help relax the throat muscles.
Painless Endoscopy with Healthy Türkiye
In conclusion, endoscopy is an essential diagnostic and therapeutic tool that allows doctors to examine the internal organs and tissues of the body. While endoscopy Turkey is generally considered to be a safe and non-painful procedure, patients may experience some discomfort or side effects. Sedation can help to alleviate anxiety and discomfort, but it may also cause drowsiness and impairment.
You can discuss the risks and benefits of endoscopy with Healthy Türkiye’s doctor before the procedure and follow the doctor's instructions for preparation and aftercare. With Healthy Türkiye, endoscopy can be a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.