CT Angiogram vs. Traditional Angiography: A Comparative Analysis
Angiograms have long been hailed as the diagnostic and therapeutic procedure par excellence for a wide range of cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Nevertheless, as a result of the expansion of new imaging technologies such as CT angiography, a great number of patients are left wondering which of the two choices is the preferable decision. This article will provide you with a comparison between computed tomography (CT) angiography and conventional (traditional) angiography in the hopes of supporting you in making an informed decision regarding the kind of examination that is most suited for you.
Which Is More Accurate CT Angiography or Angiography?
Traditional angiography and computed tomography (CT) angiography both have good accuracy rates when it comes to the detection and diagnosis of cardiovascular disorders. However, it has been demonstrated that CT angiography is more accurate than traditional methods in finding blockages in the coronary arteries. CT angiography had an accuracy rate of 93% in detecting severe coronary artery disease, but traditional angiography had an accuracy rate of 96%, according to studies. Although conventional angiography had a little greater rate of accuracy, the gap between the two methods was not statistically significant.
What Is the Difference Between a CT Angiogram and a Traditional Angiogram?
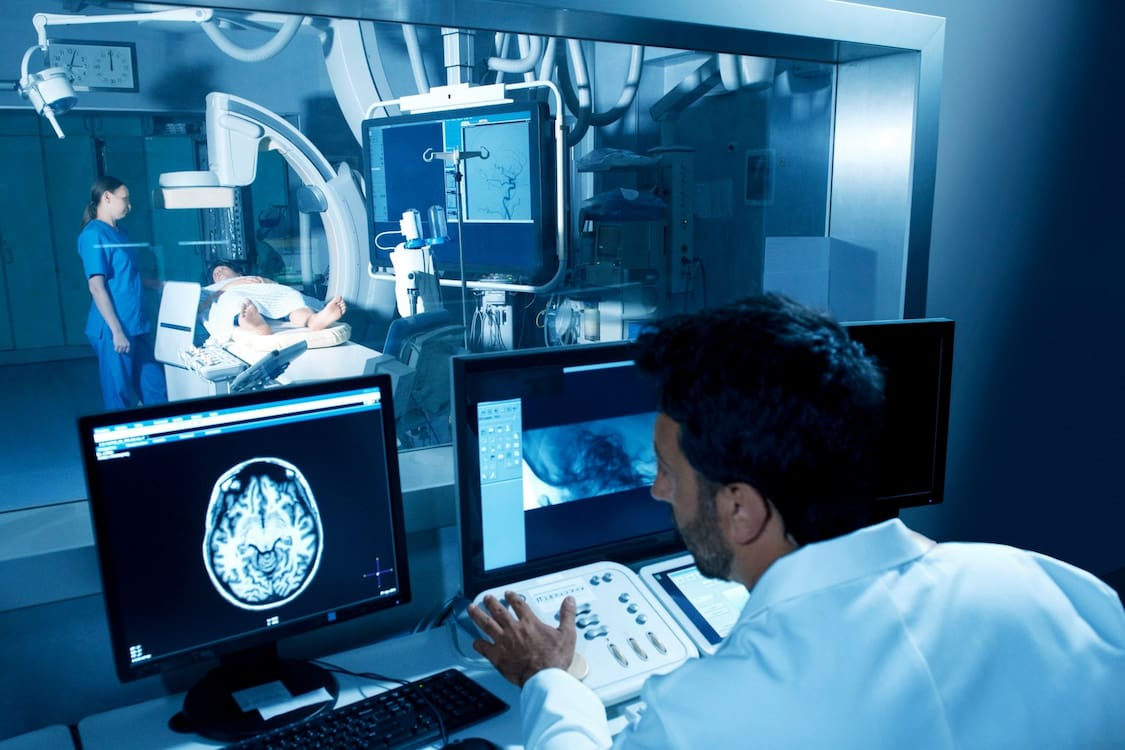
A CT angiography, also known as a CTA, is a non-invasive imaging diagnostic that produces comprehensive images of the arteries and veins in the body by using X-rays and computer technology. In order to better see the arterial structure on the pictures, a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream. This helps to highlight the artery structure and makes it easier to see. The examination is completely painless and does not call for any incisions or general anesthesia to be performed.
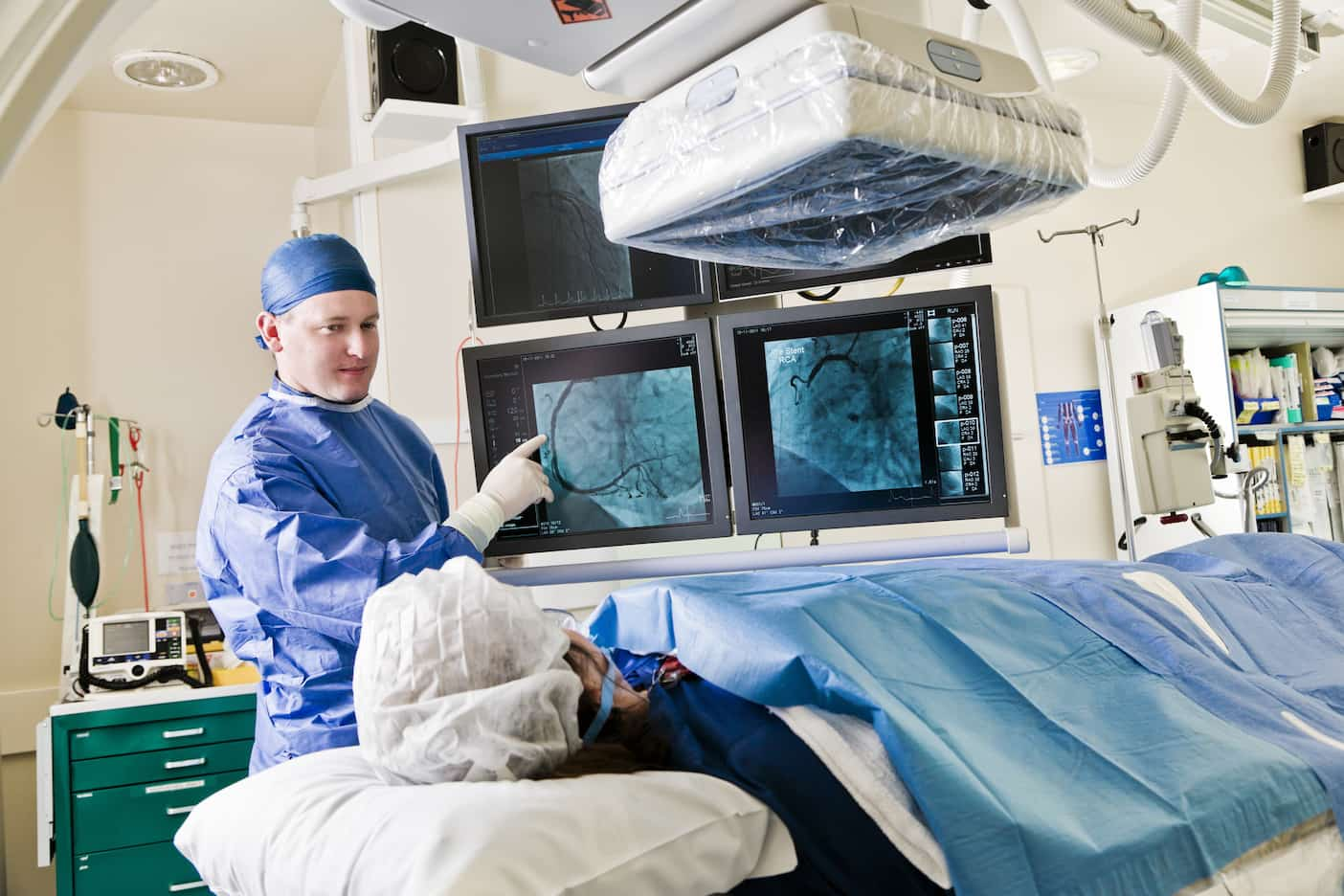
On the other hand, a conventional angiogram, also known as coronary angiography, is a more invasive treatment that includes threading a catheter, which is a thin, flexible tube, into an artery in the groin or arm and into the heart. The catheter is then used to inject a contrast dye, and X-rays are collected in order to obtain pictures of the coronary arteries. The operation, which is performed under local ananesthesiamay result in a degree of discomfort for the patient.
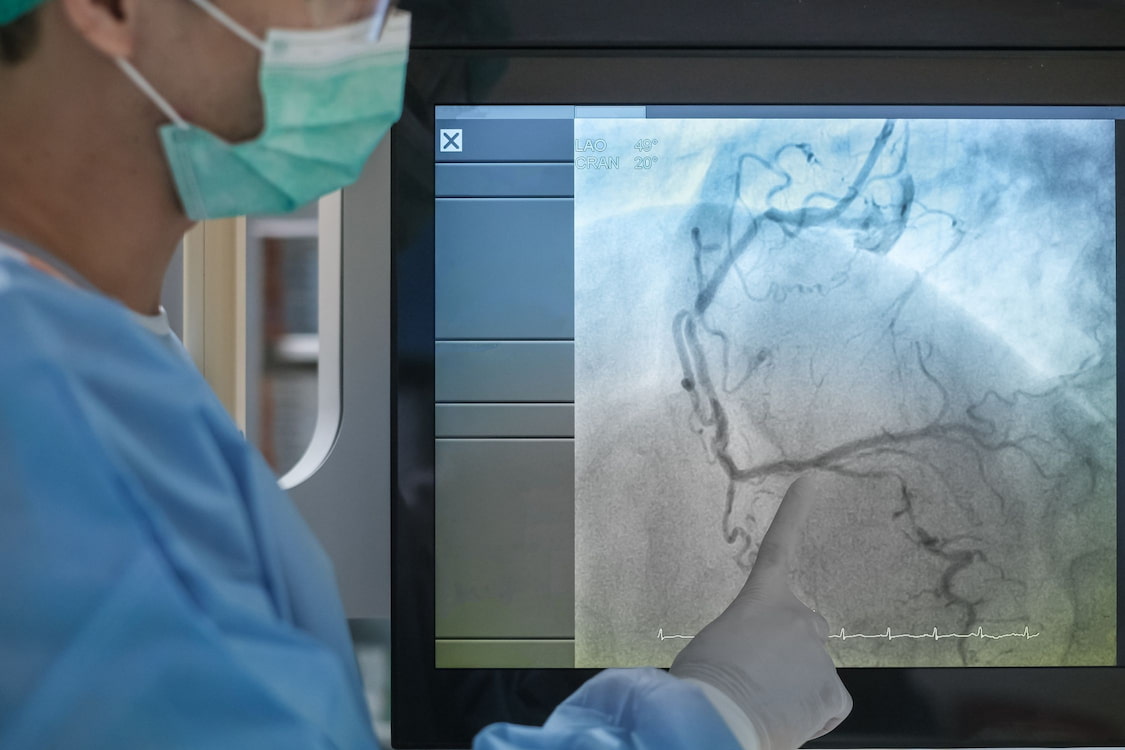
Which Angiography Is the Best for the Heart?
Traditional angiography and computed tomography (CT) angiography are both useful diagnostic tools for heart disease. On the other hand, CT angiography may be the method of choice for individuals who have a low to moderate risk of developing heart disease but who do not exhibit any obvious symptoms of the condition. This is due to the fact that it is a non-invasive test that does not require any incisions or anesthesia. Additionally, it is capable of providing accurate results without the hazards that are connected with invasive procedures.
individuals who have symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or who have had an abnormal stress test are often candidates for traditional angiography. This type of angiography is typically advised for individuals who have a high risk of heart disease. Traditional angiography can be required in these situations in order to get an accurate diagnosis of the condition that's causing the symptoms and decide which treatment method will be most effective.
Is CT Angiography Recommended?
CT angiography is a safe and effective imaging test that is recommended in many cases for diagnosing cardiovascular diseases. However, it may not be appropriate for all patients. Patients with kidney disease or allergies to contrast dye may not be able to undergo the test, as the contrast dye can cause kidney damage or an allergic reaction. Additionally, pregnant women are generally advised to avoid CT angiography, as the radiation exposure can be harmful to the developing fetus.
What Is the Disadvantage of CT Angiogram?
While CT angiography has many advantages over traditional angiography, there are some potential disadvantages to consider. One of the main drawbacks is the radiation exposure associated with the test. Although the amount of radiation is relatively low, it can still pose a risk over time, particularly for patients who undergo multiple scans. Additionally, CT angiography may not provide as clear images of the coronary arteries as traditional angiography, particularly in patients with heavily calcified arteries.
What Is the Best Test for Heart Blockage?
The specifics of each patient's condition determine which diagnostic approach is going to yield the most accurate results. CT angiography is a non-invasive diagnostic that can accurately detect blockages in the coronary arteries. Because of this, it may be the test of choice for patients who have a low to moderate risk of developing heart disease but who are not experiencing any severe symptoms. Traditional angiography may be required for patients who have a higher risk of heart disease or significant symptoms in order to precisely evaluate the cause of the symptoms and establish the most effective course of treatment for the condition.
CT coronary angiograms, also known as CTCAs, are another technique that can be used to diagnose blockages in the coronary arteries of the heart. CTCAs are a subtype of CT angiography that concentrate solely on the coronary arteries. Regular CT angiography utilizes a lower dosage of contrast dye than CTCA does, which results in less blurriness in the images of the coronary arteries produced by CTCA. However, this results in the patient being subjected to a greater quantity of radiation.
Healthy Türkiye Notes
In conclusion, conventional angiography and computed tomography angiography (CT angiography) are both reliable diagnostic tools for cardiovascular disorders. CT angiography is not intrusive, therefore it may be chosen for patients who have a low to moderate risk of heart disease. Traditional angiography, on the other hand, is more invasive but may be required for individuals who have a higher risk of heart disease or significant symptoms. CT angiography is becoming increasingly popular as a non-invasive alternative to traditional angiography. In the end, the choice of test will be determined by the specific circumstances of the particular patient, and it is recommended that this decision be made in collaboration with the patient's healthcare professional.